In codominant inheritance, ____
a. there is partial phenotypic expression of one member of a gene pair in the homozygous condition
b. there is full phenotypic expression of both members of a gene pair in the heterozygous condition
c. the interaction of two or more non-allelic genes controls a single phenotype
d. two recessive alleles interact and express themselves as a single dominant trait
e. the phenotype of a heterozygote is intermediate to those of the parents
ANSWER: b
You might also like to view...
GGG and GGC are codons for the amino acid, glycine. A mutation caused the insertion of a cytosine in place of the guanine during DNA replication. Over many generations the DNA changes so that the frequency of GGC is similar to that of GGG. What is this phenomenon called?
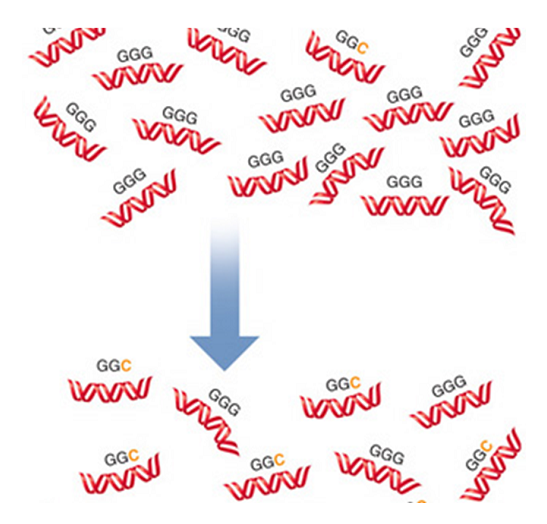
A. directional selection
B. bottleneck effect
C. stabilizing selection
D. adaptive variation
E. neutral variation
The duct between a testis and a seminal vesicle is the ____________________. Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s)
What type of mutation occurred in the following?
Normal allele GGAAUGAAACAGGAACCC Mutant allele GGAAUGAAACAGGUACCC substitution insertion deletion frameshift
Please choose the statement that best describes the immunologic basis of organ or tissue rejection after transplantation.
A) Specific T cell populations recognize non-self MHC molecules on transplanted tissue and mount a cell-mediated immune response damaging the transplant. B) Transplanted tissue is normally rejected only if it becomes infected. C) Organ/tissue transplant rejection is mostly due to Type 2 cytotoxic reactions mediated by IgG and IgM. D) IgE antibodies as well as basophils and mast cells attack the transplanted tissue if they recognize it as "non-self."