In the principal-agent model, at the employee's optimal effort choice:
A. the incentive coefficient of effort is very high.
B. the net benefits of effort are maximized.
C. the marginal benefit of effort is negative.
D. the marginal costs of efforts exceed the marginal revenue.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Suppose a powerful labor union negotiates a wage for its members above the equilibrium wage rate in a nonunionized market. A likely result of this is that
A. this firm will make up for the higher wage rate by expanding output. B. the union will have difficulty recruiting new members. C. not everyone who wants to work at the new wage will be able to find jobs. D. union members will be able to work more overtime than before.
In the table above, the marginal product of the first unit of labor is ________ units of output
A) 4 B) 5 C) 16 D) 20
Two perfectly competitive firms, Firm A and Firm B, both face random demand and have the same expected marginal revenue, as illustrated in the figure below. For which firm would a forecast of demand be more valuable?
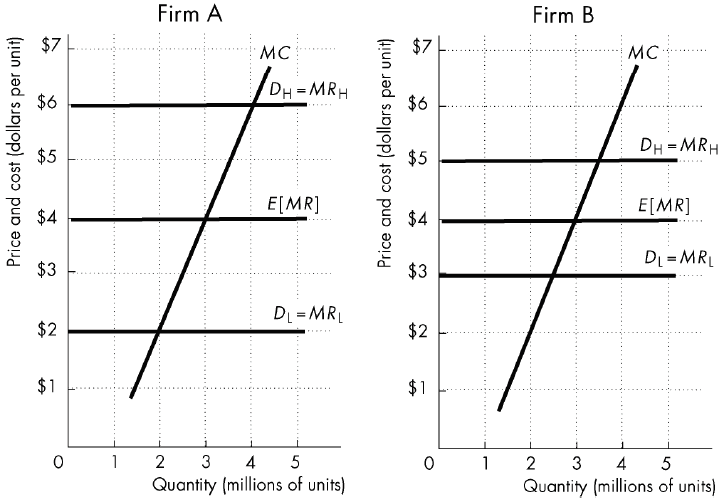
A) Firm A
B) Firm B
C) The value for each firm is the same because the expected marginal revenue and marginal cost are the same.
D) A forecast is more valuable for Firm A if the demand will be high and more valuable for Firm B if the demand will be low.
The term utility refers to the:
a. usefulness of a good in relation to its scarcity. b. necessity of a good. c. price of a good. d. number of goods a consumer has. e. pleasure or satisfaction a consumer receives upon consuming a good.