Identify the four methods of troubleshooting and list the most important feature to each.
What will be an ideal response?
There are a number of troubleshooting methods that can be used with these models. Methods vary depending on individual educational faculty, consultants, and industry. The basic approach to most methods includes the development of a good educational foundation.
Method One: Educational
• Basic knowledge of the equipment and technology
• Understanding of the math, physics and chemistry associated with the equipment
• Study equipment arrangements in systems
• Study process control instrumentation
• Operate equipment in complex arrangements
• Troubleshoot process problems
Troubleshooting is a process that requires a wide array of skills and techniques. Modern control instrumentation includes; indicators, alarms, transmitters, controllers, control valves, transducers, analyzers, interlocks, etc. The primary goal is to control variables like temperature, pressure, flow, level, or analytical variables. It is possible to control large, complex processes from a single room. In these types of systems, process set points and process variables on controllers should clearly reflect each other. Process problems are quickly identified when these two do not line up. Example: If the flow rate is set at 200 gpm and the process variable is 175 gpm, a 25 gpm difference exists. This could indicate a serious problem.
Method Two: Instrumental
• Basic understanding of process control instrumentation
• Basic understanding of the unit process flow plan
• Advanced training in controller operation- PLC & DCS
• Troubleshoot process problems
Method Three: Experiential
• Experience operating specific equipment and system
• Familiarity with past problems and solutions
• Ability to think outside the box
• Critical thinking- identify and challenge assumptions
• Evaluates, monitors, measures, tests alternatives
• Troubleshoot process problems
Method Four: Scientific
• Grounded in principles of mathematics, physics, and chemistry
• Theory-based operations
• Good understanding of equipment design and operation
• Views the problem from the outside in.
• Utilizes outside information and expertise and reflective thinking
• Generates alternatives, brainstorming, rank alternatives
• Troubleshoot process problems
You might also like to view...
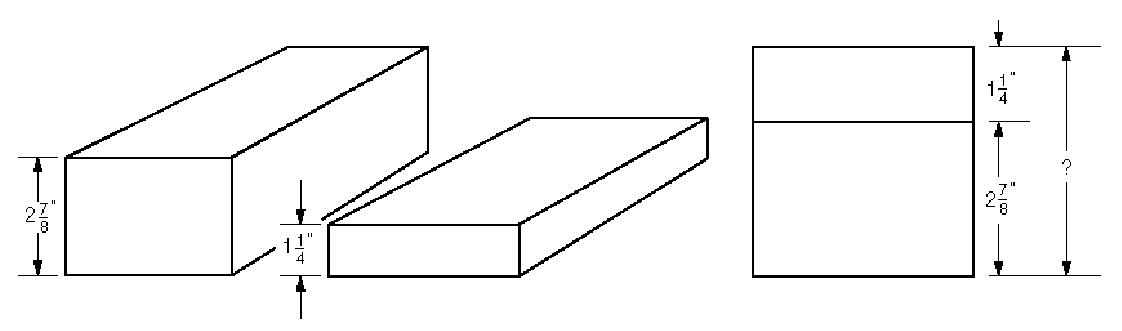
If you stack four each of these steel bars, what is the height of the stack, in inches?
Reduce all fractions to their simplest forms. Convert all improper fractions to mixed numbers. Provide answers in the following format:
Fraction: 3/4
Mixed number: 1 5/8
The schematic diagram resembles a ladder in that it is made up of two vertical lines representing the incoming electrical sources.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Both kVa and watts are ____ measurements.
A. energy B. heat C. voltage D. power
Any seed that comes into the country or that crosses a state line must be inspected for ____________________ weed seed
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word