The price of a first-class stamp in 1957 was 3 cents, and it is 49 cents in 2014. From this we know that
A) both the relative and the absolute price of first-class stamps increased from 1957 to 2014.
B) the money price of first-class stamps increased from 1957 to 2014 but the absolute price of first-class stamps stayed constant.
C) the money price of first-class stamps increased from 1957 to 2014 and the relative price of first-class stamps decreased.
D) the money price of first-class stamps increased from 1957 to 2014, but we can't tell if the relative price of first-class stamps increased or decreased without more information.
D
You might also like to view...
A firm is operating in its range of economies of scale and is on both its LRAC curve and its short-run ATC curve. At that level of output, the slope of its LRAC curve is
A) zero and the slope of its ATC curve is zero. B) zero and the slope of its ATC curve is negative. C) negative and the slope of its ATC curve is zero. D) negative and the slope of its ATC curve is negative.
A supply curve generally
a. is a straight horizontal line. b. is a straight vertical line. c. slopes downward to the right. d. slopes upward to the right.
Suppose Bright Orange is large firm that grows and harvests oranges. Each orange yields 2 ounces of orange juice and exactly one orange peel. Bright Orange sells the orange juice to juice distributors and the orange peels to fragrance companies. If the market for oranges is perfectly competitive, Bright Orange will determine its profit-maximizing output level based on ________.
A) the market price of an orange B) the market price of an ounce of orange juice C) the market price of two ounces of orange juice D) the market price of an orange peel
According to the graph shown, the equilibrium price is:
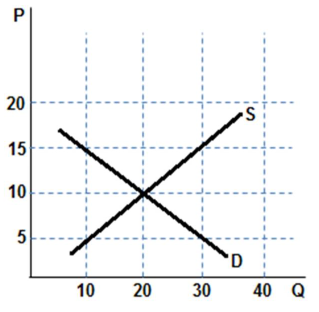
According to the graph shown, the equilibrium price is:
A. $5
B. $10
C. $15
D. $20