An electron and a proton are separated by a distance of 1 m. What happens to the size of the force on the proton if the electron is moved 0.5 m closer to the proton?
A) It increases to 4 times its original value.
B) It decreases to one-half its original value.
C) It increases to 2 times its original value.
D) It decreases to one-fourth its original value.
E) It increases to 8 times its original value.
A
You might also like to view...
What makes Iapetus different than most other Jovian satellites? a. Its surface is so eroded that it has no distinguishing surface features. b. It is not impacted by Saturn's tidal heating
c. It is perfectly spherical and highly reflective. d. It has an old and heavily cratered surface. e. It is asymmetrical and always faces backward to Saturn.
Each of the four diagrams below shows a hypothetical electric field in a certain region of empty space where the magnetic field is constant in time. 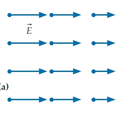 Which of the fields are physically impossible and why?
Which of the fields are physically impossible and why?
A. This field violates Faraday’s law. B. This field violates Gauss’s law. C. This field violates both of the above laws. D. This field is physically possible.
Measuring the amount of deuterium in the universe allows us to set a limit on
A) the density of ordinary (baryonic) matter the universe. B) the total amount of mass in the universe. C) the acceleration of the universe. D) the current age of the universe.
A car with good tires on a dry road can decelerate (slow down) at a steady rate of about 5.0 m/s2 when braking. If a car is initially traveling at 55 mi/h (a) how much time does it take the car to stop? (b) what is its stopping distance?
What will be an ideal response?