How are prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes different?
a. Prokaryotic genomes are loops of double stranded DNA, while eukaryotic genomes are double stranded linear DNA molecules.
b. Prokaryotic genomes are smaller than eukaryotic genomes.
c. Prokaryotic genomes are larger than eukaryotic genomes.
d. Eukaryotic genomes are loops of double stranded DNA, while prokaryotic genomes are double stranded linear DNA molecules.
a. Prokaryotic genomes are loops of double stranded DNA, while eukaryotic genomes are double stranded linear DNA molecules.
You might also like to view...
Based on a variety of experiments, it is known that the rate of photosynthesis is highest when wavelengths of light between 400 and 500 nm are used, and when wavelengths around 700 nm are used. What does this indicate about the relative importance of chlorophyll a and b in photosynthesis?
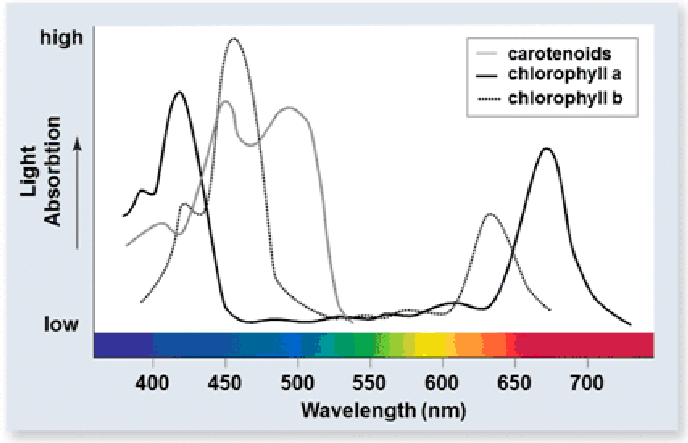
A. Reflection of light by chlorophyll a and b is essential for the process of photosynthesis
B. Absorption of light by chlorophyll a and b is essential for the process of photosynthesis
C. Transmission of light by chlorophyll a and b is essential for the process of photosynthesis
D. Chlorophyll a and b are much less important than other pigments in the reflection, absorption and transmission of light relevant to photosynthesis
Clarify Question
What is the key concept addressed by the question?
What type of thinking is required?
Gather Content
What do you already know about the role of pigments during photosynthesis? What other information is related to the question?
Choose Answer
Do you have all the information needed to analyze the graph and answer the question?
Reflect on Process
Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
All forms of phototropy "harvest" light energy to fix carbon, producing sugar.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Explain why in some cases, linked genes may be separated during crossing-over, yet at other times, linked genes are not affected by the recombination during meiosis
What will be an ideal response?
The random change in frequency of a genetic variant in a population is called
a. negative selection. b. gene conversion bias. c. purifying selection. d. genetic drift. e. positive selection.