Starting from long-run equilibrium, a war that raises government purchases results in ________ output in the short run and ________ output in the long run.
A. lower; potential
B. higher; potential
C. higher; higher
D. lower; higher
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The table below gives the quantities and prices for 2000 and 2010 for an economy that produces just two goods: sailboats and coconuts. Quantity producedPrice 2000201020002010Sailboats1020$500$525Coconuts2,0002,400$1$2For this economy that produces just sailboats and coconuts, and with 2000 is the base year, real GDP was approximately ______ times larger in 2010 than it was in 2000.
A. 1.34 B. 1.77 C. 1.65 D. 2.19
The real discount rate and the nominal discount rate differ in their treatment of
A) risk. . B) market return. C) inflation. D) expected risk.
The major tools of monetary policy available to the Federal Reserve System are
A) reserve requirements, margin regulations, and moral suasion. B) reserve requirements, open-market operations, and the discount rate. C) open-market operations, margin regulations, and moral suasion. D) the discount rate, margin regulations, and moral suasion.
Refer to the information provided in Table 23.7 below to answer the question(s) that follow. Table 23.7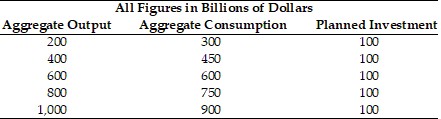 Refer to Table 23.7. Which of the following statements is false?
Refer to Table 23.7. Which of the following statements is false?
A. If aggregate output equals $1000 billion, then aggregate saving equals $100. B. The MPC for this economy is 0.75. C. At an output level of $400 billion, there is a $150 billion unplanned inventory decrease. D. At output levels greater than $800 billion, there is a positive unplanned inventory change.