A perfectly competitive firm faces a market clearing price of $150 per unit. Average total costs are at the minimum value of $120 per unit at an output rate of 70 units. Marginal cost equals $150 per unit at an output rate of 75 units. It can be
concluded that the short-run profit-maximizing output rate is
A) 75 units, at which the firm earns zero economic profits per unit sold.
B) 75 units, at which the firm earns negative economic profits per unit sold.
C) 75 units, at which the firm earns positive economic profits per unit sold.
D) 70 units, because price is less than average total costs.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Joe quits his job as an insurance agent and opens his own sporting goods store. If his profits as measured by his accountant are greater than zero, then
A) he made a good move because he is earning above normal profits. B) his economic profit must be greater than zero. C) his opportunity costs must be zero. D) There is not enough information to determine his economic profit, if any.
Which of the following is not a problem in the People's Republic of China following the economy's rapid growth?
A. income inequality B. labor issues C. lack of potential for foreign trade because of China's comparative advantage in the production of all goods D. pollution
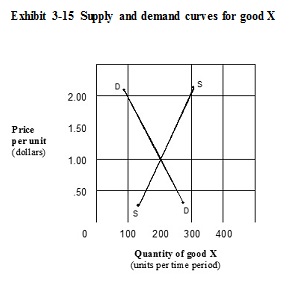
A. $0.50, 250. B. $2.00, 300. C. $2.00, 100. D. $1.00, 200.
A 10 percent rise in the price of housing reduces the quantity demanded of housing by 3 percent. We can conclude that the demand for housing is:
A. inelastic. B. elastic. C. unitary elastic. D. perfectly elastic.