What is the difference between labor's marginal product and marginal revenue product?
A) The marginal product of labor is the additional labor's contribution to the firm's total output while the marginal revenue product is the additional labor's contribution to the firm's total sales revenue.
B) Labor's marginal product is a measure of labor's productivity while labor's marginal revenue product is a measure of labor's ability to sell the firm's products.
C) The marginal revenue product of labor is the dollar value of hiring an additional worker while the marginal product of labor is the increase in the firm's physical output as a result of hiring an additional worker.
D) The marginal product of labor is the increase in output as a result of hiring an additional worker while the marginal revenue product of labor is the increase in profit as a result of hiring an additional worker.
A
You might also like to view...
When the price of a product increases, consumers shift their purchases to other products whose prices are now relatively lower. This statement describes
A. an inferior good. B. the substitution effect. C. the income effect. D. the rationing function of prices.
Exhibit 10-6 Aggregate supply curve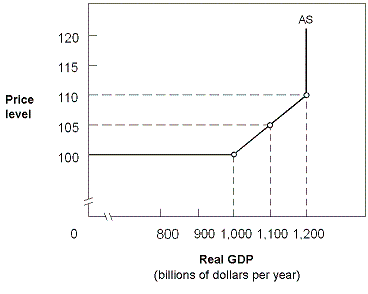
A. higher wages will lower the cost of producing goods. B. real GDP and employment both increase, but only under conditions of constant prices. C. real GDP increases and employment decreases, but only under conditions of price level increases. D. real GDP and employment both increase, but only under conditions of price level increases.
Which of the following is considered a negative supply shock?
A) increasing immigration in the economy causes the labor supply to rise B) an improvement in technology C) an increase in unemployment D) an unexpected decrease in the refining capacity for oil
If the price elasticity of demand for a good is greater than one in absolute value, economists characterize that demand is
A) elastic. B) inelastic. C) perfect. D) vertical.