Quantum issues often constrain transitions in quantum harmonic oscillators to those where ?n = 1. Consider a spectrum chart (like the one shown in figure Q11.2) for such a system. What would this chart look like?
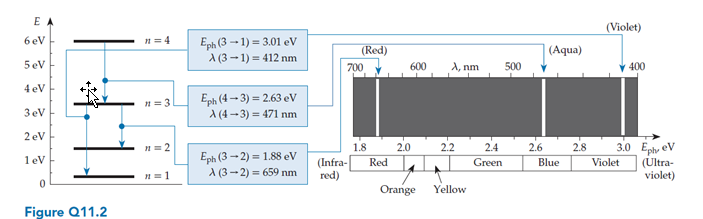
A. There would be only one emission line.
B. The emission lines would be evenly spaced in energy.
C. The emission lines would become more closely spaced (in energy) as we go to the right.
D. The emission lines would become farther apart (in energy) as we go to the right.
A. There would be only one emission line.
You might also like to view...
Constant Angular Acceleration: A machinist turns on the power on to a grinding wheel at time t = 0 s. The wheel accelerates uniformly from rest for 10 s and reaches the operating angular speed of 96 rad/s. The wheel is run at that angular velocity for 40 s and then power is shut off. The wheel slows down uniformly at 1.5 rad/s2 until the wheel stops. For how long a time after the power is shut off does it take the wheel to stop?
A. 64 s B. 62 s C. 66 s D. 68 s E. 70 s
Instructions: On occasion, the notation 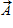
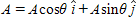
The vector 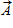
An object moving at 30 m/s has an acceleration of -2.0 m/s/hr. Its speed
A. decreases very quickly. B. decreases very slowly. C. increases very slowly. D. increases very quickly.
When the surface of a metal is exposed to blue light, electrons are emitted. If the intensity of the blue light is increased, which of the following things will also increase?
A) the number of electrons ejected per second B) the maximum kinetic energy of the ejected electrons C) the time lag between the onset of the absorption of light and the ejection of electrons D) the work function of the metal E) all of the above