Consider the following:
(i) Consider an uncrowded highway that has limited access. Is this good nonrivalrous, nonexcludable, or both? Explain.
(ii) Consider a major city's downtown streets during rush hour. Is this good nonrivalrous, nonexcludable, or both? Explain.
(i) Since the highway is uncrowded, an additional person can use the highway at no additional cost, so the highway is nonrivalrous. However, since the highway has limited access, it would be relatively easy to set up toll booths and prevent a person from using the highway. Therefore, the highway is not a nonexcludable good.
(ii) An additional person adds to the congestion of rush hour, so the use of downtown streets is not a nonrivalrous good. On the other hand, it would be extremely difficult to prevent any one person from having access to the downtown streets, so their use is nonexcludable.
You might also like to view...
In 1989, Sears and Roebuck closed its stores and remarked every price in its stores to reflect a new "lower everyday" pricing strategy. Sears must have believed at that time that
A) the profit from extra sales were less than additional menu costs. B) the menu costs were less than the gain in profits from additional sales. C) extra liquidity was more important than menu costs. D) B and C.
What is the most significant cost of attending medical school?
a. Tuition and fees. b. Books and incidentals. c. The income foregone. d. Room and board. e. Pain and suffering.
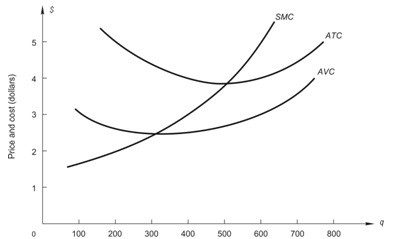 The graph above shows cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. If market price is $3, how much profit will the firm earn?
The graph above shows cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. If market price is $3, how much profit will the firm earn?
A. -$400 B. $200 C. $400 D. -$200
How do future expectations about the price of a good affect the present supply?
(A) If the price is expected to decrease, many producers will hold onto their supply. (B) If the price of a related good is expected to increase, only a few sellers will hold onto their supply until the increase occurs. (C) If the price is expected to increase, many producers will hold onto their supply. (D) If the price is expected to increase and then decrease, most sellers will hold onto their supply until the decrease has occurred.