If full-employment national income is Y = $1,500 billion and the current equilibrium national income is Y = $2,200 billion and MPC = 0.8, then to eliminate the ___________ you would have to _______________
a. recessionary gap; decrease aggregate expenditure by $140 billion
b. inflationary gap; decrease aggregate expenditure by $140 billion
c. recessionary gap; increase aggregate expenditure by $140 billion
d. inflationary gap; decrease aggregate expenditure by $700 billion
e. recessionary gap; decrease aggregate expenditure by $700 billion
B
You might also like to view...
Refer to Game Matrix III. Which of the following is a property of this game?
Game Matrix III
The following questions refer to the game matrix below. Each firm has a choice of advertising, Ads, or not advertising, No ad. The profits each gets depend upon which it chooses.
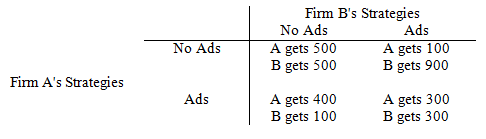
a. Both firms have dominant strategies.
b. There is no pure strategy Nash equilibrium.
c. There is a Nash equilibrium and it is Pareto optimal.
d. There is a Nash equilibrium and it is not Pareto optimal.
The IMF was
a. created during the Great Depression to regenerate trade. b. created during the Kennedy round of GATT negotiations in the 1960's. c. created at Bretton Woods to facilitate international exchange. d. abolished by President Nixon in the early 1970's.
A Keynesian short-run aggregate supply curve has a flatter portion and a steep portion. How does an increase in aggregate demand affect the price level differently across these two portions?
a. There is a sharp increase in the price level across the flatter portion and a small increase in the price level across the steep portion. b. There is a sharp decrease in the price level across the flatter portion and a small decrease in the price level across the steep portion. c. There is a small increase in the price level across the flatter portion and a sharp increase in the price level across the steep portion. d. There is a small decrease in the price level across the flatter portion and a sharp increase in the price level across the steep portion.
As real interest rates increase, other things equal, the net present value of education is likely to
A. decrease, possibly becoming negative. B. remain unchanged. C. increase. D. decrease, but necessarily remaining positive, since more knowledge is always a good thing.