If the economy were producing at point E and moved to point B the opportunity cost in terms of lost production of outboard motors would be
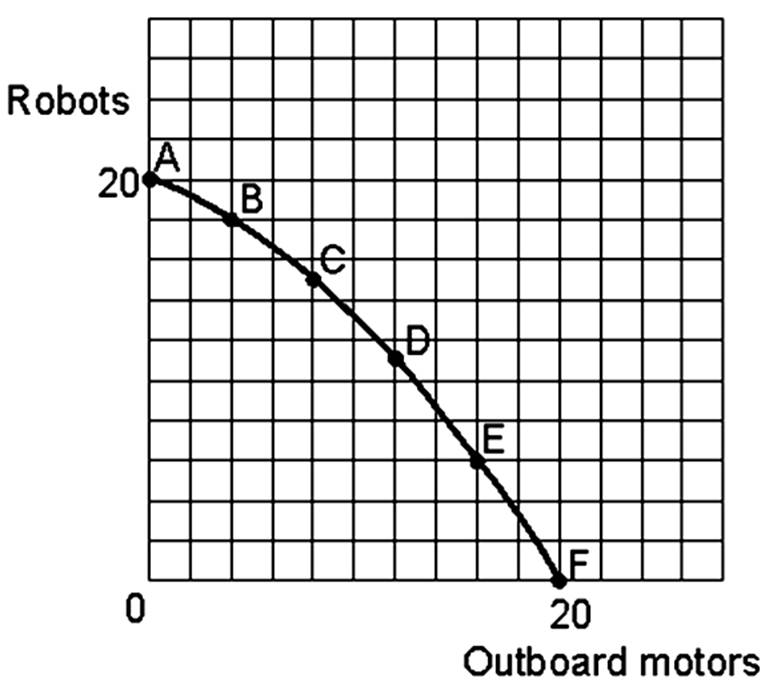
A. 16 units of outboard motors.
B. 14 units of outboard motors.
C. 12 units of outboard motors.
D. 10 units of outboard motors.
C. 12 units of outboard motors.
You might also like to view...
The above figure shows the payoff matrix facing an incumbent firm. Assuming a fixed cost of entry, will the incumbent deter entry? Why?
What will be an ideal response?
Suppose there are 10 apples and 10 oranges in the economy. Joe is currently consuming 4 apples and 5 oranges, and Jane is consuming 6 apples and 5 oranges
At this allocation, Joe's marginal utility of apples is 3, and his marginal utility of oranges is 5. Jane's marginal utility of apples is 6, and her marginal utility of oranges is 10. If the current price of apples is $4 and the current price of oranges is $5, then there is an: A) excess demand for apples and an excess supply of oranges. B) an excess demand for oranges and an excess supply of apples. C) equilibrium in the market with no excess supply or demand for either good. D) an excess supply of apples and oranges.
The substantial increase in household debt relative to income since the mid 1980s meant that in 2008 many households
a. had little savings or other reserve assets for use to deal with unexpected expenditures. b. could safely afford to purchase larger homes because housing is always a good investment. c. could spend everything they earned because their interest obligations on outstanding credit were low. d. would be able to easily adjust their current spending if their monthly payments on adjustable rate mortgages rose.
Why might reforms to encourage saving lead to a less egalitarian society?