Long-run macroeconomic policies concentrate on:
A) minimizing fluctuations around potential GDP.
B) maximizing fluctuations around potential GDP.
C) incentives for increasing productivity and the potential output of the economy.
D) none of the above.
C
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, an increase in government spending that increases aggregate demand from AD to AD1 will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ creating _____gap. 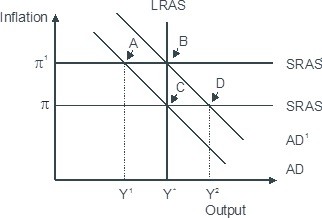
A. D; an expansionary B. B; no output C. B; expansionary D. A; a recessionary
The time-inconsistency problem involves the ________
A) difficulties of traveling across time zones B) tendency to deviate from good long-run plans in the short-run C) use of adaptive expectations in building an economic model D) time lag between the implementation of policy and its ultimate and complete results
Joe's income is $500, the price of food (F) is $2 per unit, and the price of shelter (S) is $100. Which of the following represents his budget constraint?
A) 500 = 2F + 100S B) F = 250 - 50S C) S = 5 - .02F D) All of the above
If aggregate demand increases and, as a result, the price level increases but equilibrium real GDP and employment remain unchanged, we can assume that the aggregate demand curve
A. intersects the upward-sloping segment of the aggregate supply curve. B. intersects the vertical segment of the aggregate supply curve. C. intersects the horizontal segment of the aggregate supply curve. D. is horizontal.