Refer to the figure and assume the economy initially is in equilibrium at point a. In the new classical theory, an unanticipated decrease in aggregate demand from AD 2 to AD 3 would move the economy:
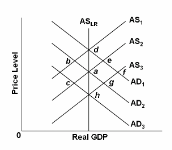
A. directly from a to h.
B. from a to g to h.
C. directly from a to d.
D. from a to c to h.
D. from a to c to h.
You might also like to view...
The Pacific Pulp Company plans to clearcut 100 acres of land to produce paper pulp which would earn the firm $50,000 in profits. One hundred nearby homeowners realize that this would reduce the value of each of their properties by $1,000. These 100 homeowners
a. face a logistical problem of getting together to offer a bribe to Pacific Pulp. b. would not benefit from offering any side payment to Pacific Pulp not to clearcut. c. have no legal option except to suffer the damages to their property values. d. can costlessly organize to offer Pacific Pulp a side payment not to clearcut.
The principle economic cost of growth is
A. higher inflation rates. B. higher interest rates. C. investment in stocks and bonds. D. current consumption sacrificed for capital formation.
A perfect market would have all but which of the following characteristics?
A) Infinitely divisible securities B) Asymmetric information C) Buyers and sellers of financial instruments would know the true quality of what they are buying and selling. D) Buyers and sellers could transact with each other without cost (no transactions costs).
Which of the following statements best reflects the production decision of a profit-maximizing firm in a competitive price-taker market when price falls below the minimum of average variable cost?
a. The firm will continue to produce to attempt to pay fixed costs. b. The firm will stop production to minimize its losses. c. The firm will stop production as soon as it is able to pay its sunk costs. d. The firm will continue to produce in the short run but will likely exit the market in the long run.