Figure 4-23
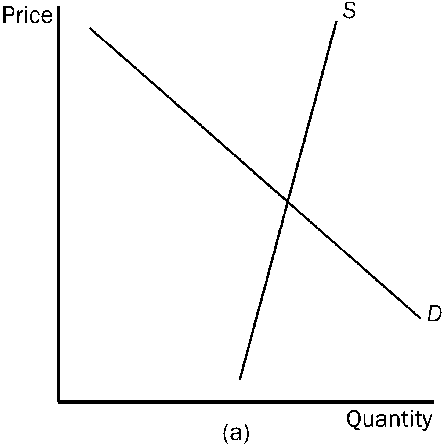
Refer to . In which market will the tax burden be most equally divided between the buyer and the seller?
a.
market (a)
b.
market (b)
c.
market (c)
d.
All of the above are correct.
c
You might also like to view...
In each of the following situations, list what will happen to the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity for a particular product, which is a normal good
a. The price of inputs decrease b. The price of a complement increases c. The number of producers in the market increases d. Income increases e. The price of a substitute in production increases
The basic Keynesian argument for discretionary monetary policy is that
A) monetary policy is the principal cause of business cycles. B) monetary policy is much more effective than fiscal policy. C) aggregate demand is unstable and monetary policy can help to stabilize it. D) reducing unemployment is much more important than reducing inflation.
If perfect competition existed everywhere, along with frictionless exchange, perfect information, and constant returns to scale,
a. consumers would carry out transactions directly with resource suppliers b. firms would not have the information necessary to calculate marginal productivities of resources c. entrepreneurs would be needed to collect information d. consumers would produce output and then engage in barter e. the economy would be organized into one large firm
Which of the following is the best example of market failure?
A. Alex and others in a community want a new outdoor soccer field and are willing to pay to use it, but no private business is willing to build it. B. Lucian wants more video games but doesn't buy them because his willingness to pay is less than the equilibrium price in the market. C. Kara's Kitten Shop won't sell more purebred cats because the equilibrium price in the market is less than it would cost her to provide more. D. Government fixes the price of gasoline, resulting in a shortage.