Which areas of the globe would likely be mapped on a planar projection, and why?
Figure 4.5a shows Earth on a planar projection, in which the globe is projected onto a plane. This is a gnomonic projection and is generated by projecting a light source at the center of a globe onto a plane that is tangent to (touching) the globe’s surface. The resulting increasingly severe distortion as distance increases from the standard point prevents showing a full hemisphere on one projection.
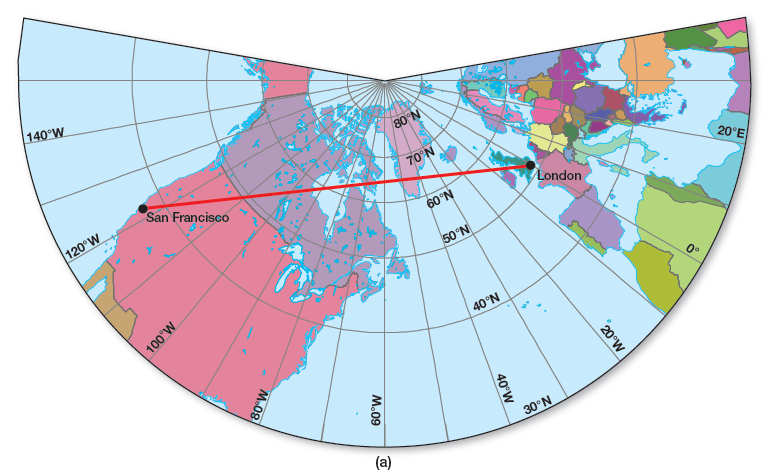
Figure 4.5 (a) Gnomonic/planar projection
Used for high latitude/polar regions (Arctic/Antarctic); closest to point of tangency
You might also like to view...
The plant shown in the photograph below is an invasive species that often clogs waterways in the southeastern United States. It is the

A) lily pad.
B) coypu.
C) water hyacinth.
D) cottonmouth.
How does a supercell thunderstorm differ from a multicell thunderstorm?
What will be an ideal response?
Spits and baymouth bars are formed due to ____________________ currents. Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s)
Why are abyssal plains not as well developed in the Pacific Ocean as they are in the Atlantic Ocean?
a) The deep ocean trenches of the Pacific Ocean act like gutters that trap sediment transported off the land by turbidity currents b) Turbidity currents travel directly down the continental margin and deposit sediment c) Abyssal plains occur only in Earth's eastern hemisphere d) Organisms disrupt deposition of fine sediment in the Pacific Ocean basin e) Suspension settling in the Pacific Ocean occurs much faster than in the Atlantic Ocean