Refer to the graph shown. Suppose an economy begins at point B but then adopts a contractionary monetary policy. In the long run, this policy would most likely: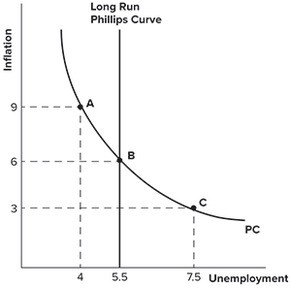
A. lower inflation to 3 percent but raise unemployment to 7.5 percent.
B. lower inflation to 3 percent but leave unemployment at 5.5 percent.
C. raise inflation to 9 percent but lower unemployment to 4 percent.
D. raise inflation to 9 percent but leave unemployment at 5.5 percent.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Using economic theory to analyze policy issues
A. is a way to avoid inconvenient facts. B. allows researchers to disprove a hypothesis. C. relies on simplifications to conduct studies. D. always includes the inclusion of political ideals.
A bond with no expiration has an original price of $10,000 and a fixed annual interest payment of $1,000. If the price of this bond increases by $2,500, the interest rate in effect will
A. decrease by 1 percentage point. B. increase by 1 percentage point. C. increase by 2 percentage points. D. decrease by 2 percentage points.
Average cost curves have the same basic shape as
A. total cost curves. B. marginal cost curves. C. total fixed cost curves. D. average fixed cost curves.
The high cost of advertising during the Super Bowl will
A) not affect the efficient level of output because advertising is a sunk cost. B) will affect the efficient level of output because profits will fall significantly. C) not affect the efficient level of output because advertising is a fixed cost. D) Not enough information given.