How does a change in the quantity of money change the interest rate in the long run?
What will be an ideal response?
In the long run a change in the quantity of money does not change the interest rate. For example, suppose the Federal Reserve increases the quantity of money (the effects from a decrease in the quantity of money are the reverse of an increase). In the short run the nominal interest rate and the real interest rate fall. Both households and firms increase their demand for goods. The resulting shortages force prices higher and therefore the price level rises. As the price level rises, the quantity of real money decreases, which raises the nominal interest rate and real interest rate. The rise in the interest rate decreases the demand for goods. Eventually the price level rises so that the quantity of real money equals the initial amount. At this point, the nominal interest rate and real interest rate have risen to equal their initial values so there is no long-run effect on the interest rate from a change in the quantity of money.
You might also like to view...
Consider a production possibility frontier with books and tables. A combination of 1000 books and 500 tables is on the frontier. Which of the following are true?
i. Production of 700 books and 400 tables is attainable but inefficient. ii. Production of 1000 books and 600 tables is unattainable. iii. Production of 500 books and 1000 tables is inside the frontier. A) i, ii and iii B) i only C) i and iii D) ii and iii E) i and ii
The above figure shows a firm in monopolistic competition. At the profit maximizing level of output, excess capacity for the firm is equal to
A) 0 units per day. B) 4 units per day. C) 8 units per day. D) 16 units per day.
If a pair-wise majority vote was held and the voters' preferences are shown in the table, assuming public parks and the zoo was the first pair to be voted on, which option would win overall?
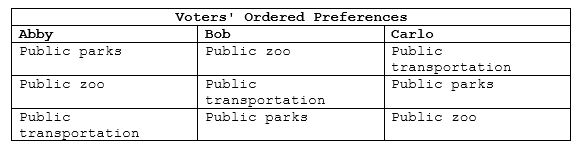
A. Public transportation
B. Public zoo
C. Public parks
D. Both Public parks and zoo.
In the 1950s, W. Phillips investigated the relationship between
A. wage and price inflation. B. the unemployment rate and the rate of change in interest rates. C. the unemployment rate and the rate of change in prices. D. output and price changes.