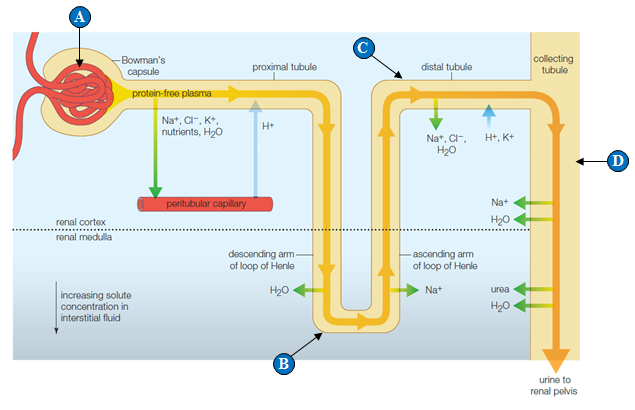
Figure 40.7
Where does hormonal adjustment to solute and volume levels occur?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. C and D
Answer: E
You might also like to view...
The question of whether animal eyes have evolved independently in different organisms or have evolved once from a single organism and then diverged over time is still being actively investigated by evolutionary scientists
A. true B. false
Ranking questions: Put the steps in the correct order for a birder hearing the call of a whip-poor-will.
__ basilar membrane vibrates in different regions for each note __ action potentials travel down axons that represent different frequencies __ bird sings "whip-poor-will" __ cilia of hair cells bend in different regions for each note __ sound waves travel to the birder's pinna and enter the canal __ pressure waves travel through fluid in the cochlea __ auditory cortex interprets the pattern __ tympanic membrane vibrates __ malleus, incus, and stapes vibrate __ oval window vibrates Clarify Question What is the key concept addressed by the question? What type of thinking is required? Gather Content What do you already know about hearing? What other information is related to the question? Choose Answer Given what you now know, what information is most likely to produce the correct answer? Reflect on Process Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
The major characteristics that uniquely identify each chromosome in a karyotype are the
A. types of proteins, number of telomeres, and banding pattern. B. size, number of telomeres, and banding pattern. C. sequence of nitrogen bases, types of proteins, and banding pattern. D. centromere position, banding pattern, and size. E. position and orientation, types of proteins, and genes.
Which protein functions to break down clots after wounds heal?
A) prothrombin B) thrombin C) fibrinogen D) plasmin