Monopolies misallocate resources because
A) price does not equal marginal cost.
B) price does not equal average variable cost.
C) marginal cost does not equal average total cost.
D) profits are usually positive.
A
You might also like to view...
The accompanying diagram shows the U.S. market for automobiles. P0 is the world price of automobiles, Q0 is the quantity of American automobiles produced, and Q1 - Q0 is the quantity of automobiles imported. Consumers are indifferent between American and imported automobiles, but each imported automobile creates $100 of pollution costs.
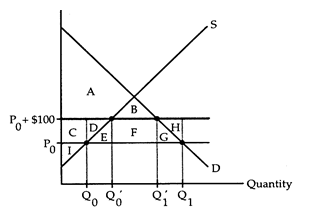
(i) Calculate consumers' surplus, producers' surplus, the pollution damages, and social gain when no attempt is made to internalize the externality.
(ii) Suppose the government imposes a $100 tariff on imported automobiles. Calculate consumers' surplus, producers' surplus, tariff revenue, the pollution damages, and social gain in this situation. Did the tariff increase social gain? Did the tariff result in an efficient outcome? Explain.
Suppose Sam plans to buy only popcorn and soda. He has $40 to spend per week. A change in which of the following variables will change Sam's consumption possibilities? I. price of popcorn II. income III. preferences IV. utility
A) II only B) I and II C) I, II and III D) III and IV
Federal Reserve Chairman Volcker's policy to fight inflation
A) led to the 1981-1983 recession, but was ultimately successful. B) led to the 1981-1983 recession, but did not end high inflation due to beggar-thy-neighbor effects. C) was perfectly complemented by Reagan's decrease in fiscal spending. D) led to the 1981-1983 recession and foretold the economic downturn in the mid-1990s. E) led to an immediate depreciation of the dollar.
The higher the opportunity cost of borrowing, the higher the amount of investment, other things constant
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false