During the financial crisis of 2008-2010, the Fed increased its purchases of securities and extended more loans, which caused the monetary base to
a. increase rapidly, but the M1 money supply declined because the banks loaned out most of the additional reserves to businesses.
b. fall, but the M1 money supply still expanded rapidly because the banks increased their loans to businesses.
c. increase rapidly, but the M1 money supply expanded at a much slower rate because the banks enlarged their excess reserves.
d. fall, and this led to a sharp decline in the M1 money supply.
C
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, a decrease in government spending that decreases aggregate demand from AD1 to AD will lead to a short-run equilibrium at__ creating _____gap.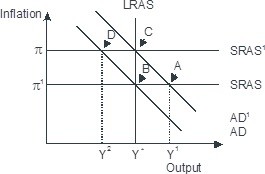
A. B; no output B. D; an expansionary C. B; recessionary D. D; a recessionary
If a nation has a higher level of technology than another nation it can produce:
A. more outputs with the same level of physical capital. B. less with the same amount of physical capital. C. more with no use of human capital. D. the same output with the same level of inputs.
The larger the MPC: a. the smaller the multiplier
b. the smaller the effect of a given increase in government purchases on consumption purchases. c. the larger the effect of business taxes which reduce investment on aggregate demand. d. the less powerful changes in individual taxes will be in changing aggregate demand.
Suppose that Canada decides to peg its dollar ($C, or the loonie) to the U.S. dollar at an exchange rate of $C1 = $US1. What might the U.S. Federal Reserve do to offset the macroeconomic effect of the leftward shift in the U.S. IS curve?
A) It would increase the money supply. B) It would decrease the money supply. C) It would not change its monetary policy. D) It would not change its fiscal policy