The model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply can NOT be used to:
A. discuss the pros and cons of income tax cuts.
B. evaluate a tax cut's effect on short run economic fluctuations.
C. assess a tax cut's effect on longer run issues such as the national debt.
D. to discuss income distribution.
D. to discuss income distribution.
You might also like to view...
The long-run aggregate supply curve is the relationship between the quantity of real GDP supplied and ________ when ________
A) the price level; real GDP equals potential GDP B) real GDP demanded; the wage rate is constant C) the price level; real GDP equals nominal GDP D) real GDP demanded; the price level does not change
Banks do not create money when they make loans
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
State and local government spending as a share of GDP has: a. decreased from 12% in 1960 to about 8% in 2014
b. increased from 12% in 1960 to about 20% in 2014. c. remained more or less stable at 12% between 1960 and 2014. d. increased from 20% in 1960 to about 30% in 2014.
Hotelling's model has been used to describe differentiation in the political "market." Suppose that 100 voters are evenly distributed between the extreme left and the extreme right on the political spectrum, and that all voters vote, and they always vote for the candidate closest to them on this spectrum. The numbers on this spectrum represent the number of voters lying to the left of the number. So, at the midpoint, fifty voters lie to the left and fifty to the right. At the extreme right end, all 100 voters lie to the left. 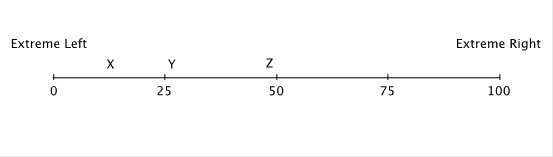 To an economic naturalist, this model helps explain why political candidates:
To an economic naturalist, this model helps explain why political candidates:
A. are loyal to their political parties. B. work to bring federally funded projects to their home districts. C. move toward more centrist positions during campaign season. D. take more extreme positions than are held by the general population.