Your company makes copper pipes. Over the years, you have collected a large inventory of raw copper. The production process involves melting the copper and shaping it into pipes. You also have a large stockpile of pennies. Suppose the price of copper rises so much that the copper in the penny becomes worth more than one cent. Should you melt down your pennies?
What will be an ideal response?
This problem appeared as a puzzle in the Journal of Economic Perspectives (Winter, 1988). It is true (in this problem) that the pennies when melted currently have a value greater than one cent. Yet, the price of copper can fluctuate. If the price of copper stays high, it does not matter if you melt pennies or not. However, if the price of copper falls so that the value of the copper in the penny falls below one cent, your unmelted pennies are still worth one cent. Your melted pennies would be worth less than one cent. Thus, as long as you have some other source of copper, you are better off melting that copper and not the pennies.
You might also like to view...
Evaluate the overall tax incidence of state and local taxes in contrast with federal taxes. In addition, what can be concluded about the overall tax system?
What will be an ideal response?
The largest category of money-market instrument is
A) commercial paper. B) U.S. Treasury bills. C) corporate bonds. D) corporate stock.
Which of the following is not an institution used by government to secure rights?
a. The police. b. The military. c. The courts. d. The copyright office.
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as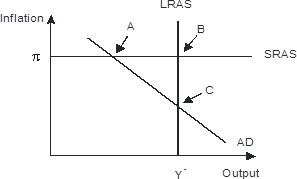
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward C. Aggregate demand shifting rightward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward