Prices are likely to be least flexible:
A. in oligopoly.
B. in monopolistic competition.
C. where product demand is inelastic.
D. in pure competition.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Over what range of prices does a surplus arise? What happens to the price when there is a surplus?
What will be an ideal response?
If the price of a good is low,
a. firms would increase profit by increasing output. b. the quantity supplied of the good could be zero. c. the supply curve for the good will shift to the left. d. firms can and should raise the price of the product.
Use the following graph, where Sd and Dd are the domestic supply and demand for a product and Pc is the world price of that product, to answer the next question.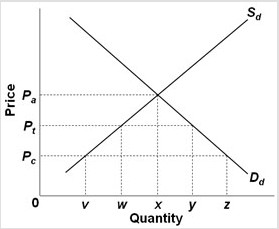 With a per-unit tariff in the amount Pt?Pc, price and total quantity sold will be
With a per-unit tariff in the amount Pt?Pc, price and total quantity sold will be
A. Pc and z. B. Pa and x. C. Pt and x. D. Pt and y.
In the short run the individual competitive firm's supply curve is the segment of the:
A. marginal cost curve lying between the average total cost and average variable cost curves. B. average variable cost curve lying below the marginal cost curve. C. marginal cost curve lying above the average variable cost curve. D. marginal revenue curve lying below the demand curve.