In a liquid at a given temperature, the molecules are moving in every direction, some fast, some slowly. Electrical forces of adhesion tend to hold them together
However, occasionally one molecule gains enough energy (as a result of collisions) so that it pulls loose from its neighbors and escapes from the liquid. Which of the following can best be understood in terms of this phenomenon? A) Increasing the atmospheric pressure over a liquid will cause the boiling temperature to decrease.
B) If snow begins to fall when you are skiing, you will feel colder than you did before it started to snow.
C) When a large steel suspension bridge is built, gaps are left between the girders.
D) When you step out of a swimming pool and stand in the wind, you will get colder than you would if you stayed out of the wind.
E) A hot water bottle will do a better job of keeping you warm than will a rock of the same mass heated to the same temperature.
D
You might also like to view...
If the ________ is good, the atmosphere is stable, and image quality is sharp
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
A child, whose weight is 150 newtons, lifts a pumpkin from the ground with a force of 50 newtons. The force the pumpkin exerts on the child is
A. 50 newtons. B. zero. C. more than 50 newtons. D. greater than zero but less than 50 newtons.
Determine the excess temperature at one-half of the maximum heat flux for the fluid- surface combinations in Problem 9.3.
GIVEN
? Nucleate pool boiling on a clean surface
FIND
The excess temperature (?Tx) at one half of the maximum heat flux for (a) water at 10 kPa on brass (b) water at 1 MPa on brass
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
From Appendix 2, Table 13, for water Table 9.2 for surface tension
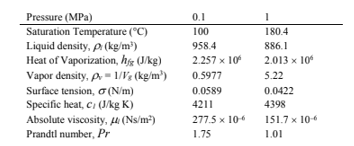
From Table 9.1, the coefficient, Csf, for water on brass = 0.0060
Contrast a hypernova and a type II supernova
What will be an ideal response?