The real interest rate can be estimated by:
A. subtracting the pure interest rate from the nominal interest rate.
B. dividing the nominal interest rate by the consumer price index.
C. subtracting the nominal interest rate from the rate of inflation.
D. subtracting the rate of inflation from the nominal interest rate.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Which macroeconomic model dominated macroeconomic analysis from the early post-World War II era until the late 1960s?
a. The monetarist model b. The Keynesian model c. The classical model d. The new classical model e. None of the above
Assume individuals consider only the long run effects of changes in future macro variables when forming expectations of future output and future interest rates. Suppose current government spending increases and that individuals expect future government spending to increase. Given this information, we know with certainty that
A) current output and the current interest rate will both increase. B) current output will not change. C) future expected output will decrease. D) future expected output will not change.
At age 40, Joe is considering quitting his job and going back for a college degree. He needs two more years full-time. Tuition is $10,000 per year. He earns $30,000 per year. A college degree would raise his annual income by $10,000 per year. He will retire at age 70. Which of the following makes it less likely that Joe will decide to go back to college full-time?
A) The extra income due to a college degree rises. B) The rate of interest decreases. C) The government enacts mandatory retirement at age 60. D) Tuition decreases.
Refer to the information provided in Table 24.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow.Table 24.5All Numbers are in $ Million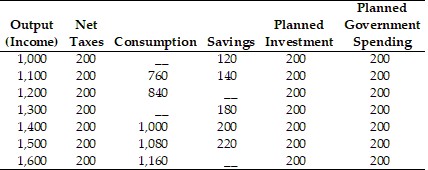 Refer to Table 24.5. Suppose the economy is in equilibrium and the government raises taxes from $200 million to $220 million, equilibrium output will ________ by $________ million.
Refer to Table 24.5. Suppose the economy is in equilibrium and the government raises taxes from $200 million to $220 million, equilibrium output will ________ by $________ million.
A. decrease; 80 B. increase; 20 C. decrease; 20 D. increase; 80