Blood is taken from each of n individuals to be tested for a certain disease. Rather than test each sample separately, a pooled method is used in an attempt to reduce the number of tests needed. Part of each blood sample is taken, and these parts are combined to form a pooled sample. The pooled sample is then tested. If the result is negative, then none of the n individuals has the disease, and no further tests are needed. If the pooled sample tests positive, then each individual is tested to see which of them have the disease.
a. LetX represent the number of tests that are carried out. What are the possible values of X?
b. Assume that n=4 individuals are to be tested, and the probability that each has the disease, independent of the others, is p=0.1. Find 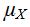 .
.
c. Repeat part (b) with n=6 and p=0.2.
d. Express 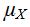 as a function of n and p.
as a function of n and p.
e. The pooled method is more economical than performing individual tests if 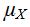 < n. Suppose n=10. For what values of p is the pooled method more economical than performing n individual tests?
< n. Suppose n=10. For what values of p is the pooled method more economical than performing n individual tests?
(a) If the pooled test is negative, it is the only test performed, so X = 1. If the pooled test is positive, then n additional tests are carried out, one for each individual, so X = n + 1. The possible values of X are therefore 1 and n + 1.
(b) The possible values of X are 1 and 5. Now X = 1 if the pooled test is negative. This occurs if none of the individuals has the disease. The probability that this occurs is 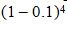 = 0.6561. Therefore P(X = 1) = 0.6561. It follows that P(X = 5) = 0.3439.
= 0.6561. Therefore P(X = 1) = 0.6561. It follows that P(X = 5) = 0.3439.
So 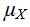 = 1(0.6561) + 5(0.3439) = 2.3756.
= 1(0.6561) + 5(0.3439) = 2.3756.
(c)The possible values of X are 1 and 7. Now X = 1 if the pooled test is negative. This occurs if none of the individuals has the disease. The probability that this occurs is 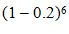 0.262144. Therefore P(X = 1) = 0.262144. It follows that P(X = 7) = 0.737856.
0.262144. Therefore P(X = 1) = 0.262144. It follows that P(X = 7) = 0.737856.
So 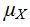 = 1(0.262144) + 7(0.737856) = 5.4271.
= 1(0.262144) + 7(0.737856) = 5.4271.
(d)The possible values of X are 1 and n + 1. Now X = 1 if the pooled test is negative. This occurs if none of the individuals has the disease. The probability that this occurs is
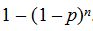 Therefore P(X = 1) =
Therefore P(X = 1) = 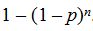 . It follows that P(X = n + 1) = 1 –
. It follows that P(X = n + 1) = 1 – 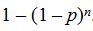
So 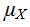 = 1
= 1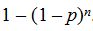 + (n + 1)(1 – (1 – p)n) = n + 1 – n
+ (n + 1)(1 – (1 – p)n) = n + 1 – n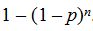 .
.
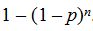
(e) The pooled method is more economical if 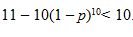 . Solving for p yields p< 0.2057.
. Solving for p yields p< 0.2057.
You might also like to view...
?CADD files are created as models and ____.
A. ?forms B. ?blocks C. ?templates D. ?sheets
A memory cache on the processor chip is called a(n) ____ cache.
A. External B. Internal C. Secondary D. Execution
The type of compound commonly called 20-minute mud, 30-minute mud, or hot mud is _____ compound
a. timed b. minute c. quickset d. premix
What is the sum of 6 3/8", 4 3/16", and 5 7/8"?
What will be an ideal response?