The economy of Appleland is experiencing a recession. In the figure given below, AD represents aggregate demand and AS represents aggregate supply in Appleland.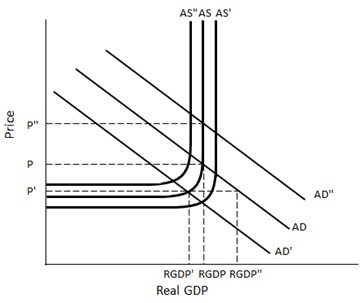 From the Keynesian point of view, Appleland's austerity policy
From the Keynesian point of view, Appleland's austerity policy
A. increase its price level to P''.
B. does not cause any change in its price level.
C. does not cause any change in its real GDP.
D. decrease its real GDP to RGDP'.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Average variable cost can be calculated using any of the formulas below except
A) ?(TC - FC)/?Q. B) TVC/Q. C) (TC - FC)/Q. D) (TC/Q) - AFC.
Altruism describes:
A. a motive for action in which a person's utility is unaffected when another's utility increases. B. a motive for action in which a person's utility is decreased when another's utility increases. C. a motive for action in which a person's utility is increased when another's utility increases. D. a motive for action in which a person's utility becomes negative when another's utility increases.
Fiscal policy:
a. Is a powerful tool because budget deficits add directly to Aggregate Demand with no offsetting changes in consumption, investment, and/or net exports. b. May not be a powerful tool if most government expenditures are fixed and unchangeable in the short run. c. Is not a powerful tool because the government has very little control over a nation's monetary base and/or money multiplier. d. Is a powerful tool because of the decisive movements in the automatic stabilizers.
Unrestricted entry and exit into the market is found in
A. perfect competition, monopolistic competition and oligopoly. B. perfect competition and oligopoly. C. monopolistic competition and oligopoly. D. perfect competition and monopolistic competition.