What happens at a firm's point of saturation?
A) For the first time, hiring an additional worker decreases total product.
B) Workers cannot take on any additional tasks without working overtime hours.
C) The market for a firm's output has been saturated and sales fall to zero.
D) The firm's total costs exceed its revenues.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
"Gasoline purchases were up 10% last week, even though gasoline prices were 6 cents higher than the week before! You see, the law of demand does not hold for gasoline!" What is being misunderstood in the above statement?
A) Nothing at all. B) It implies the demand curve for gasoline is vertical. C) It fails to recognize that the demand curve has shifted to the right. D) It fails to hold constant all the other factors that influence demand.
Standby passengers on airlines who pay low rates for seats benefit from the low price. How are the airlines affected?
A. They lose, because the standby passengers do not cover the full cost of the seats. B. They gain, because the additional revenue covers the “fixed costs” of the flight. C. They lose, because the gain of the passengers must necessarily come at the expense of the airline. D. They benefit as long as the additional revenue from the passengers exceeds the marginal cost. E. Uncertain, because economic theory says nothing about this sort of situation.
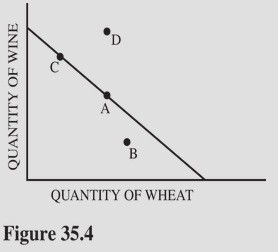 Refer to Figure 35.4 for the production possibilities curve for Chile: Chile's production and consumption of wine and wheat without trade are represented by point A. Suppose that Chile has a comparative advantage in the production of wine compared to the United States and specialization and trade take place between the two countries. The most likely new combination of wine and wheat available to Chile would be
Refer to Figure 35.4 for the production possibilities curve for Chile: Chile's production and consumption of wine and wheat without trade are represented by point A. Suppose that Chile has a comparative advantage in the production of wine compared to the United States and specialization and trade take place between the two countries. The most likely new combination of wine and wheat available to Chile would be
A. D. B. A. C. C. D. B.
The slope of a straight line
A) is the same at all points along that line. B) cannot be defined. C) changes from one point to the next on that line. D) is always equal to zero.