When water changes from a vapor phase to a liquid phase, it
A) loses energy.
B) gives off energy.
C) gains energy.
D) radiates energy.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Addition by 1. Components: Vector src="https://sciemce.com/media/4/ppg__cp1pbb0313192044__f15g1q20g6.jpg" style="vertical-align: -5.0px;" /> is given by
A. 2.0 m at an angle 63° north of east.
B. 2.0 m at an angle 63° east of north.
C. 6.7 m at an angle 63° east of north.
D. 6.7 m at an angle 63° north of east.
E. 3.8 m at an angle 67° north of east
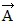 has a magnitude of 8.0 m and points east, vector
has a magnitude of 8.0 m and points east, vector 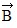 has a magnitude of 6.0 m and points north, and vector
has a magnitude of 6.0 m and points north, and vector 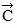 has a magnitude of 5.0 m and points west. The resultant vector
has a magnitude of 5.0 m and points west. The resultant vector 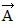 +
+ 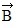 +
+
As shown in the above spectra, which is taken at two different times, a ________ is concluded
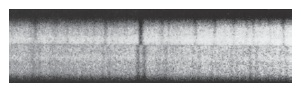
a. visual binary
b. eclipsing binary
c. spectroscopic binary
d. single star
Suppose that a ship is accelerating through space in such a way that the passengers are experiencing a constant force (due to the thrust of the ship) equivalent to the total weight of the ship and passengers on Earth
From the point of view of observers on Earth, how does the ship accelerate? A) It has a constant acceleration of 9.8 m/s2, therefore increasing its speed by 9.8 m/s with each passing second. B) At first, it has a nearly constant acceleration of 9.8 m/ s2. But as it approaches the speed of light, its acceleration gradually slows in such a way that it never stops accelerating, but never reaches the speed of light either. C) At first, it has a very large acceleration—much larger than 9.8 m/s2. But when it reaches the speed of light it stops accelerating. D) It has a constant acceleration of 9.8 m/s2 until it reaches a speed of half the speed of light. Then its acceleration suddenly slows so that it can't go much faster.
Which moons of our solar system are sometimes called the Galilean moons?
A) the four largest moons of Jupiter: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto B) the two largest moons in the solar system: Ganymede and Titan C) the moons that orbit their planet "backward" compared to their planet's rotation, such as Neptune's moon Triton D) the moons orbiting Uranus, which was once named "planet Galileo"