Consider the simultaneous choice game represented by the matrix below where Player A chooses either Up or Down and Player B chooses either Left or Right.
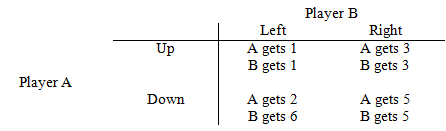
i. Discuss whether or not either player has a dominant strategy.
ii. Identify the Nash equilibrium in the game and explain why you have concluded that it is a Nash Equilibria.
iii. Now imagine that the game could be played sequentially. If Player A gets to choose their strategy first, can they do better than in the sequential game than in the equilibrium from the simultaneous game? Explain.
i. Player A has a dominant strategy of choosing Down. Player B does not have a dominant strategy.
ii. The Nash Equilibrium is for Player A to choose Down and Player B to choose Left. This is because from A’s perspective, 2 > 1 and from B’s perspective 6 > 5.
iii. If Player A chooses Up, then Player B will select Right since 3 > 1. If Player A chooses Down, then Player B will choose Left since 6 > 5. So, if Player A chooses Up, they will ultimately get a payoff of 2 whereas by choosing Up, they will get a payoff of 3. Therefore, Player A can be better off in the sequential game because it gives them the ability to credibly commit to playing Up, the result of which is a payoff of 3 rather than the payoff of 2 that they earn in the Nash equilibrium of the simultaneous game.
You might also like to view...
All of the following are examples of nonpoint source pollution EXCEPT
a. urban runoff c. agricultural runoff b. sulfur emissions from power plants d. snowmelt from city streets
If Congress and the president pursue an expansionary fiscal policy at the same time as the Federal Reserve pursues an expansionary monetary policy, how might the expansionary monetary policy affect the extent of crowding out in the short run?
What will be an ideal response?
Government attempts to set prices below market equilibrium can:
A. lead to more producer surplus. B. encourage more production. C. reduce the total surplus in the market. D. always create a better outcome.
An increase in the U.S. GDP will result in
A. an increase in exports of the United States. B. an increase in imports of the United States. C. an increase in the dollar exchange rate and a decrease in imports of the United States. D. an increase in the dollar exchange rate and a rise in imports of the United States.