A salesperson for insulation material claims that insulating exposed steam pipes in the basement of a large hotel will be cost effective. Suppose saturated steam at 5.7 bars flows through a 30-cm- OD steel pipe with a 3 cm wall thickness. The pipe is surrounded by air at 20°C. The convective heat transfer coefficient on the outer surface of the pipe is estimated to be 25 W/(m2 K). The cost of generating steam is estimated to be $5 per 109 J and the salesman offers to install a 5 cm thick layer of 85% magnesia insulation on the pipes for $200/m or a 10-cm-thick layer for $300/m. Estimate the payback time for these two alternatives assuming that the steam line operates all year long and make a recommendation to the hotel owner. Assume that the surface of the pipe as well as the
insulation have a low emissivity and radiative heat transfer is negligible.
GIVEN
Steam pipe in a hotel basement
Pipe outside diameter (Do) = 30 cm = 0.3 m
Pipe wall thickness (Ls) = 3 cm = 0.03 m
Surrounding air temperature (T?) = 20°C
Convective heat transfer coefficient (hc) = 25 W/(m2 K)
Cost of steam = $5/109J
Insulation is 85% magnesia
FIND
Payback time for
(a) Insulation thickness (LIa) = 5 cm = 0.05 m; Cost = $200/m
(b) Insulation thickness (LIb) = 10 cm = 0.10 m; Cost = $300/m
Make a recommendation to the hotel owner.
ASSUMPTIONS
The pipe and insulation are black (? = 1.0) The convective resistance on the inside of the pipe is negligible, therefore the inside pipe surface temperature
is equal to the steam temperature The pipe is made of 1% carbon steel Constant thermal conductivities
SKETCH
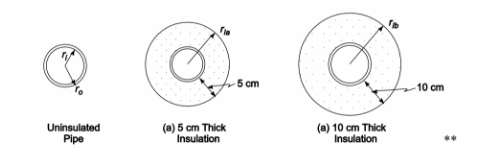
The rate of heat loss and cost of the uninsulated pipe will be calculated first.
The thermal circuit for the uninsulated pipe is shown below
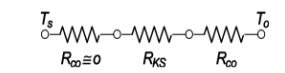
Evaluating the individual resistances
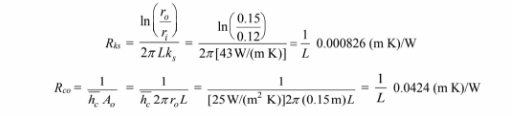
The rate of heat transfer for the uninsulated pipe is
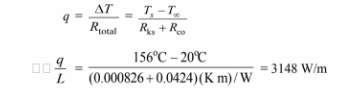
The cost to supply this heat loss is
cost = (3148 w/m) (J/W s) (3600 s/h) (24 h/day) (365 days/yr) ($5/109J) = $496/(yr m)
For the insulated pipe the thermal circuit is
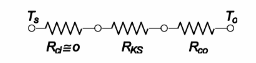
The resistance of the insulation is given by:
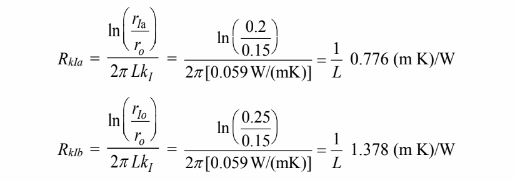
(a) The rate of heat transfer for the pipe with 5 cm of insulation is
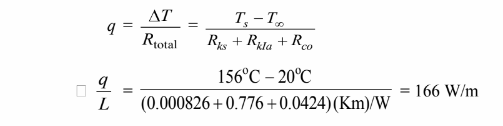
The cost of this heat loss is
cost = (166 w/m) (J/W s) (3600 s/h) (24 h/day) (365 days/yr) ($5/109J) = $26/yr m
Comparing this cost to that of the uninsulated pipe we can calculate the payback period

Payback period = 0.43 yr = 5 months
(b) The rate of heat loss for the pipe with 10 cm of insulation is
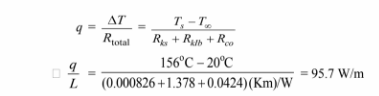
The cost of this heat loss
cost = (95.7 w/m) (J/W s) (3600 s/h) (24 h/day) (365 days/yr) ($5/109J) = $15/yr m
Comparing this cost to that of the uninsulated pipe we can calculate the payback period
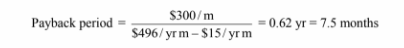
You might also like to view...
A wheel rotates about a fixed axis with a constant angular acceleration of 4.0 rad/s2 . The diameter of the wheel is 40 cm. What is the linear speed of a point on the rim of this wheel at an instant when that point has a total linear acceleration with a magnitude of 1.2 m/s2?
a. 39 cm/s b. 42 cm/s c. 45 cm/s d. 35 cm/s e. 53 cm/s
A hydrogen atom is in the 6h state. Which of the following could be an orbital quantum number?
A) 5 B) 6 C) 7 D) 8 E) 9
________ are star-like objects that contain less than 0.08 solar masses and will never raise their core temperatures high enough that the proton-proton chain can begin. Other minor fusion reactions do occur in these objects. They fall in a gap between the low-mass M dwarf stars and the massive planets in which nuclear fusion never occurs
a. Brown dwarfs b. Herbig-Haro objects c. Bok globules d. T-Tauri star e. Main-sequence stars
Where did comets that are now in the Kuiper belt originally form?
A) in the asteroid belt B) inside Jupiter's orbit C) between the orbits of Jupiter and Neptune D) near the distance at which they orbit today E) in the Oort cloud