An example of countercyclical fiscal policy is:
A. raising government spending when the economy is above potential.
B. reducing government spending when the economy is below potential.
C. raising government spending when the economy is at potential.
D. reducing government spending when the economy is above potential.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is always wrong, regardless of what other information may be given to you?
a. Hiring a worker when her marginal physical product is decreasing. b. Hiring a worker when her marginal physical product is positive. c. Hiring a worker when her marginal physical product is increasing. d. Hiring a worker when her marginal physical product is negative. e. Hiring a worker when her MRP > W.
Price elasticity of demand refers to the ratio of the:
A. percentage change in price of a good in response to a percentage change in quantity demanded. B. percentage change in price of a good to a percentage increase in income. C. percentage change in the quantity demanded of a good to a percentage change in its price. D. percentage change in the quantity demanded of a good to a percentage change in income.
Financial capital is highly volatile, and technological advances have reinforced this volatility
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Refer to the diagram that shows the market for U.S. health care. Other things equal, which of the following would shift the demand curve for medical care from D 1 to D 2 ?
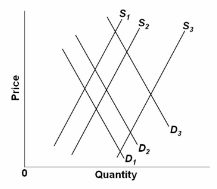
A. Higher copayments and deductibles in insurance policies.
B. An aging population.
C. Cutbacks in the government's Medicaid program.
D. Restrictions by firms on the eligibility of part-time workers for medical benefits.