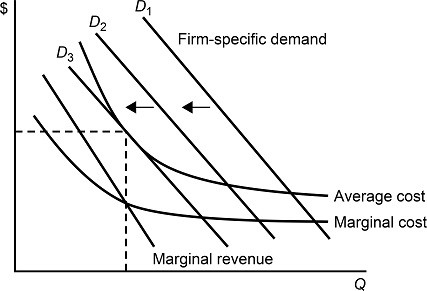
 Figure 11.3Figure 11.3 shows demands and costs for a monopolistically competitive firm. When the firm's demand curve shifts from D1 to D2 and to D3:
Figure 11.3Figure 11.3 shows demands and costs for a monopolistically competitive firm. When the firm's demand curve shifts from D1 to D2 and to D3:
A. the firm's economic profit remains the same.
B. the firm's marginal revenue at the profit maximizing output level is decreasing.
C. the firm's marginal cost at the profit maximizing output level is increasing.
D. the firm's average cost at the profit maximizing output level is decreasing.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
The opportunity cost of an apartment in a rent controlled market is equal to
A) the rent charged for the apartment. B) the opportunity cost of searching for the apartment. C) the rent charged for the apartment plus the opportunity cost of searching for the apartment. D) nothing because of the surplus of apartments when there are rent controls. E) the rent charged for the apartment minus the opportunity cost of searching for the apartment.
Throughout U.S. history, entrepreneurial activity would occur when
(a) centralized economic planning was involved (b) distributed rights to profits were clear and protected (c) government intervention was pervasive (d) all of the above
Other things equal, for a given tax, if the demand curve is more elastic,
a. the greater the tax revenue raised and the greater the deadweight cost of the tax. b. the greater the tax revenue raised and the smaller the deadweight cost of the tax. c. the less the tax revenue raised and the greater the deadweight cost of the tax. d. the less the tax revenue raised and the smaller the deadweight cost of the tax.
Which of the following is not a reason that the CPI overstates the cost of living?
A. The location of typical purchases is not adequately updated. B. There are too infrequent updates of the market basket. C. Substitution into nearly-equivalent goods is assumed to be more common than it is. D. Quality improvements are not adequately incorporated.