A heat flux meter at the outer (cold) wall of a concrete building indicates that the heat loss through a wall of 10 cm thickness is 20 W/m2 . If a thermocouple at the inner surface of the wall indicates a temperature of 22°C while another at the outer surface shows 6°C, calculate the thermal conductivity of the concrete and compare your result with the value in
IVEN
• Concrete wall
• Thickness (L) = 100 cm = 0.1 m
• Heat loss (q/A) = 20 W/m2
• Surface temperature
? Inner (Ti) = 22°C
? Outer (To) = 6°C FIND
• The thermal conductivity (k) and compare it to the tabulated value
ASSUMPTIONS
• One dimensional heat flow through the wall
• Steady state conditions exist
SKETCH
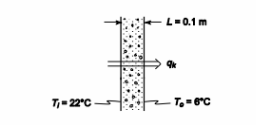
The rate of heat transfer for steady state, one dimensional conduction,
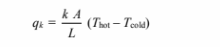
Solving for the thermal conductivity
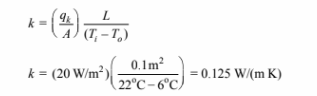
This result is very close to the tabulated value in Appendix 2, Table 11 where the thermal
conductivity of concrete is given as 0.128 W/(m K).
You might also like to view...
The electric field shown is produced by a single point charge at the center of the picture
 If a new positive point charge is placed at location A directly to the right of the one pictured, the force on it will a. be zero. b. push it to the right. c. push it to the left. d. be in an unknown direction.What is the molarity of a solution that contains 2 mol of solute in 4 L of solution?
An umbrella has a tendency to move upward when it is windy principally because
1) moving air over the curved surface produces reduced pressure against its top. 2) air moves up into the "bowl" and pushes upward with increased pressure. 3) buoyancy increases with increasing wind speed. 4) the umbrella is simply pushed upward by the wind. This effect was first accurately described by 5) Galileo. 6) Newton. 7) Bernoulli. 8) Einstein. 9) Archimedes.
The end stage of the life cycle of an extremely high-mass star is a
a. quasar. b. neutron star. c. black hole. d. white dwarf.