A flexible exchange rate is an exchange rate whose value:
A. varies according to supply and demand for the currency in the foreign exchange market.
B. reflects the comparative advantage of the home country versus other foreign countries.
C. is established annually by the International Monetary Fund.
D. is determined by the law of one price.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Always There Wireless is wireless monopolist in a rural area. There are 200 customers, each of whom has a monthly demand curve for wireless minutes of Qd = 200 - 100P, where P is the per-minute price in dollars and Q is the number of wireless minutes. The marginal cost of providing the wireless service is $0.25 per minute. If Always There charges $0.25 per minute, how large of a fixed monthly fee can it charge and still persuade customers to buy their service?
A. $200 B. $153.13 C. $306.25 D. $175
After a major ice storm left 90,00 . New York utility customers without power in January 1998, generators that normally sold for $500 were being sold for as much as $3,000 . New York law prohibits raising prices for necessities in emergency situations
Elevated prices prompted the State Attorney's office to promise to prosecute price gougers. a . Explain how this law prevents markets from clearing. Does it create a price floor or a price ceiling? b. How might antiprice gouging legislation actually work to keep people cold longer?
Which of the following shows the demonstration effect?
a. Ads that reveal the weak points of advertising b. Ads that make consumers want something they never wanted before c. Ads that push products that need to be shown how to use d. Ads that cause controversy among critics of advertising
This graph reflects a Keynesian viewpoint. How would the economy respond to an aggregate demand increase under the classical model?
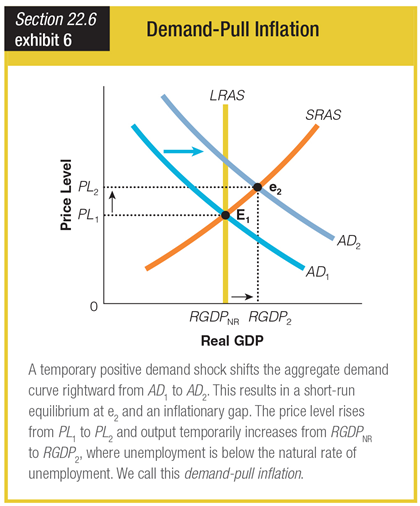
a. The economy would quickly adjust to a new point of long-run equilibrium where AD2 intercepts LRAS.
b. The shift from AD1 to AD2 would produce a short-run equilibrium point at e2 that differs from E1.
c. The economy would quickly adjust to a new point of long-run equilibrium where AD1 intercepts LRAS.
d. The shift from AD1 to AD2 would also shift LRAS rightward to a new position at RGDP2.