The impact on world well-being of an export subsidy and a countervailing duty (of the same size as the subsidy) is
A. negative due to overproduction.
B. negative due to under-consumption.
C. negative due to deadweight loss.
D. zero.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The economy pictured in the figure below has a(n) ________ gap with a short-run equilibrium combination of inflation and output indicated by point ________. 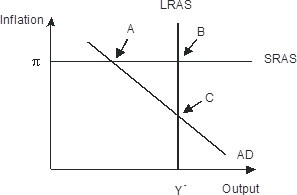
A. recessionary; B B. recessionary; C C. recessionary; A D. expansionary; A
In 1886, what did the U.S. Supreme Court rule in Wabash, St. Louis, and Pacific Railway v Illinois?
(a) Only the federal government could regulate commerce across states. (b) Only the states had the right to regulate commerce across states. (c) Neither the federal or state governments had the right to regulate across states. (d) Railroads were not subject to any government regulation, state or federal.
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, an increase in government spending that increases aggregate demand from AD to AD1 will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ creating _____gap. 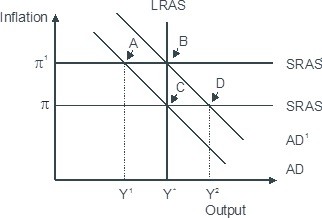
A. D; an expansionary B. B; no output C. B; expansionary D. A; a recessionary
Imagine a scandal that finds the officers of bond rating agencies have been taking bribes to inflate the rating of specific bonds. This should:
A. decrease the demand for all bonds. B. have no impact on the bond market since bond markets are highly efficient. C. decrease the risk spread. D. increase the demand for U.S. Treasury securities and decrease the demand for corporate bonds.