According to the Keynesian approach, an increase in taxes
A) will not impact consumption, as most consumption is autonomous.
B) will reduce consumption by an amount less than the change in taxes.
C) will increase consumption, as the government will spend the extra tax revenue and that increases consumption.
D) will reduce consumption exactly by the amount of the taxes.
B
You might also like to view...
According to this Application, the recessions in 1973 and 1979 were caused by
A) foreign monetary developments. B) deflation. C) arbitrage losses in the foreign exchange market. D) supply shocks.
A policy intended to reduce unemployment by taking advantage of a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment leads to
a. both higher inflation and higher unemployment in the long run. b. higher inflation and no change in unemployment in the long run. c. the same inflation rate and lower unemployment in the long run. d. higher inflation and lower unemployment in the long run
Figure 14-6
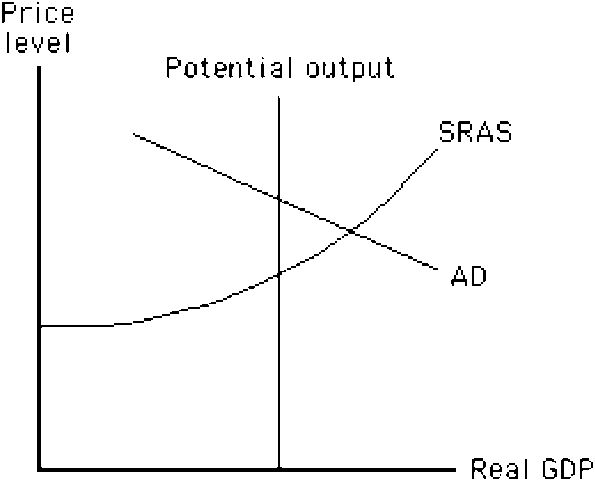
In the situation shown in , how could the Fed return the economy to potential output?
a.
decrease government spending
b.
decrease taxes
c.
sell U.S. government bonds to banks
d.
lower the discount rate
e.
lower the required reserve ratio
The demand curve for labor would shift leftward as the result of:
A. an increase in the price of the product labor is producing. B. a decrease in the productivity of labor. C. an increase in the price of labor. D. a decrease in the price of capital, provided the output effect exceeds the substitution effect.