The cross price elasticity between A and B is 1.2. We can conclude that
A. goods A and B are unrelated.
B. goods A and B are substitutes.
C. goods A and B are complements.
D. goods A and B are perfect substitutes.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Suppose two companies, Macrosoft and Apricot, and considering whether to develop a new product, a touch-screen t-shirt. The payoffs to each of developing a touch-screen t-shirt depend upon the actions of the other, as shown in the payoff matrix below (the payoffs are given in millions of dollars). 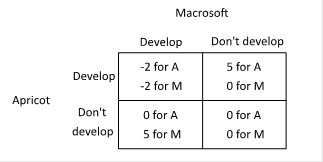 Which of the following statements is correct?
Which of the following statements is correct?
A. Apricot's dominant strategy is to not develop a touch screen t-shift. B. Apricot's dominant strategy is to develop a touch-screen t-shirt. C. Apricot does not have a dominant strategy. D. Apricot's dominant strategy is to develop a touch-screen t-shirt if Macrosoft does not.
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Using fewer observations will strengthen the force of an empirical argument. B) The number of observations used does not affect the strength of an empirical argument. C) Empirical arguments can be supported without the use of data. D) Using a large data set will strengthen the force of an empirical argument
When external benefits are present in a market,
a. less of the good will be produced than the amount consistent with economic efficiency. b. more of the good will be produced than the amount consistent with economic efficiency. c. the amount of the good produced will be equal to the amount consistent with economic efficiency. d. corresponding external costs are always generated.
Suppose we were analyzing the pound per Swiss franc foreign exchange market. If Switzerland's tax level rises relative to England and nothing else changes, then the:
a. The supply of Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market falls, and the demand for Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market rises, causing an appreciation of the Swiss franc. b. The supply of Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market rises, and the demand for Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market falls, causing an appreciation of the Swiss franc. c. The supply of Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market rises, and the demand for Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market falls, causing a depreciation of the Swiss franc. d. The supply of Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market rises, and the demand for Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market rises, causing an uncertain change in the value of the Swiss franc. e. Neither supply nor demand in the foreign exchange market change because relative international prices influence trade flows and not the exchange rate.