What happens to aggregate demand as the price level increases?
a. It increases.
b. It decreases.
c. It remains constant.
d. It moves away from equilibrium.
b. It decreases.
You might also like to view...
Quantitative easing refers to a policy action in which a central bank
A) sells government securities to directly decrease bank reserves. B) decreases interest rates directly without altering bank reserves. C) increases interest rates directly without altering bank reserves. D) buys government securities to directly increase bank reserves.
If an economy is at equilibrium, it will also be operating at full employment
a. True b. False
Which of these arises when an individual listens to loud music late in the night?
a. An externality b. The free-rider problem c. An asymmetric information problem d. The common-pool problem
Which of the following describes how import quotas on sugar generally affect producer surplus as shown in Exhibit 2?
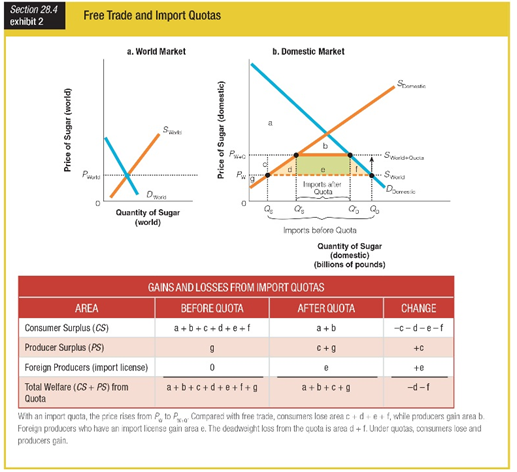
a. eliminated
b. unchanged
c. decreased
d. increased