The difference between the federal budget deficit and the national debt is that the:
a. deficit is a stock variable and the debt is a flow variable.
b. deficit is a flow variable and the debt is a stock variable.
c. debt includes interest payments and the deficit does not.
d. deficit can be positive, but the debt can not
e. debt can be negative, but the deficit cannot.
b. deficit is a flow variable and the debt is a stock variable.
You might also like to view...
Because consumers who have insurance provided by their employers usually only pay a deductible for a visit to the doctor's office, they ________ of health care services than they would if they paid a price that better represented the true cost of
providing the service. A) supply a smaller quantity B) demand a smaller quantity C) demand a larger quantity D) supply a larger quantity
Which of the following situations is descriptive of the existence of a negative externality.
A. Vernon studies for his biology test late into the night and oversleeps the next morning, thus missing the test. B. Nancy is in the library looking for a book. She is talking to herself and consequently disturbs a few people in the library. C. Bob learns later that he could have purchased a pair of shoes for less than he paid. D. Jackie has had the flu and has stayed in bed for a week. E. none of the above
Economic growth can be especially fast in countries that are playing catch-up to other countries with higher GDP per capita. As a result many economists have suggested a general principle known as the convergence hypothesis. It says that differences in real GDP per capita among countries tend to narrow over time because countries that start with lower real GDP per capita tend to have higher growth rates. Assume that this hypothesis is true. Illustrate the convergence hypothesis by using the line tool to draw an appropriate straight line, label it as the catch-up line. On this line use the point tool to plot points to represent two countries: one with a higher growth rate (label it B) and one with a lower growth rate (label it A).
What will be an ideal response?
Use the figure below to answer the following question.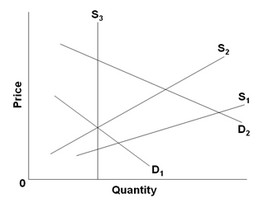 The diagram concerns supply adjustments to an increase in demand (D1 to D2) in the immediate period, the short run, and the long run. In the long run, the increase in demand will
The diagram concerns supply adjustments to an increase in demand (D1 to D2) in the immediate period, the short run, and the long run. In the long run, the increase in demand will
A. increase both equilibrium price and quantity. B. increase equilibrium price but not equilibrium quantity. C. have no effect on either equilibrium price or quantity. D. increase equilibrium quantity but not equilibrium price.