When the labor market is in equilibrium so that the quantity of labor supplied equals the quantity demanded,
A) there is no unemployment.
B) the economy is at full employment.
C) nominal GDP equals real GDP.
D) there is no inflation.
E) real GDP might be more than, less than, or equal to potential GDP.
B
You might also like to view...
Joe is the owner of the 7-11 Mini Mart, Sam is the owner of the SuperAmerica Mini Mart, and together they are the only two gas stations in town. Currently, they both charge $3 per gallon, and each earns a profit of $1,000. If Joe cuts his price to $2.90 and Sam continues to charge $3, then Joe's profit will be $1,350, and Sam's profit will be $500. Similarly, if Sam cuts his price to $2.90 and Joe continues to charge $3, then Sam's profit will be $1,350, and Joe's profit will be $500. If Sam and Joe both cut their price to $2.90, then they will each earn a profit of $900. You may find it easier to answer the following questions if you fill in the payoff matrix below. 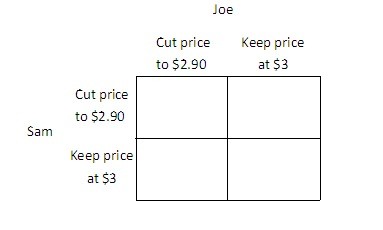
width="383" />In this situation, the Nash equilibrium yields a: A. lower payoff than each would receive if each played his dominated strategy. B. the same payoff that each would receive if each played his dominated strategy. C. lower payoff than each would receive if each played his dominant strategy. D. higher payoff than each would receive if each played his dominant strategy.
The practice of charging different prices to different consumers of the same product is called
a. monopolistic pricing b. unit pricing c. price discrimination d. elasticity pricing e. marginal cost pricing
In combating stagflation, a government-induced:
a. increase in aggregate demand would help reduce inflation but aggravate unemployment. b. decrease in aggregate demand would help reduce unemployment but aggravate inflation. c. increase in aggregate demand would help reduce unemployment but aggravate inflation. d. decrease in aggregate demand would help reduce both unemployment and inflation. e. increase in aggregate demand would help reduce both unemployment and inflation.
Which of the following is not a problem for less-developed countries?
a. Poor health and nutrition. b. Shortages of labor. c. High unemployment rates. d. Low labor productivity. e. low life expectancy