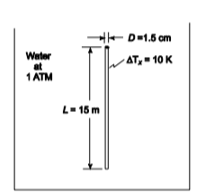
Predict the nucleate-boiling heat transfer coefficient for water boiling at atmospheric pressure on the outside surface of a 1.5-cm-OD vertical copper tube 1.5-m-long. Assume the tube-surface temperature is constant at 10 K above the saturation temperature.
GIVEN
? Water boiling at atmospheric pressure on the outside surface of vertical copper tube
? Tube outside diameter (D) = 1.5 cm = 0.015 m
? Tube length (L) = 1.5 m
? Tube surface temperature above saturation temperature (?Tx) = 10 K
FIND
? The nucleate-boiling heat transfer coefficient (hb)
ASSUMPTIONS
? The water is at saturation temperature
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
From Appendix 2, Table 13, for saturated water at 1 atm (Tsat = 100°C)

As stated near the end of Section 9.2.2, ‘the geometric shape of the heating surface has no appreciable
effect on the nucleate boiling mechanism’.
Assuming the boiling is nucleate boiling, the heat flux q", is given by Equation (9.2)

Rearranging

The critical heat flux for nucleate boiling is given by Equation (9.4)
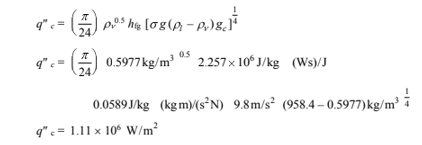
Since q" < q”c, the nucleate boiling assumption is valid.
By definition
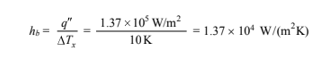
You might also like to view...
A(n) ____ is one in which an object orbiting Earth has an orbital period equal to the rotation period of Earth
A) epicyclical orbit B) open orbit C) geosynchronous orbit D) heliocentric orbit
As water changes to ice, water molecules
A) absorb energy. B) release energy. C) retain their energy. D) lose the quality of wetness.
A certain source of sound waves radiates uniformly in all directions. At a distance of 20 m from the source the intensity level is 51 db. What is the total acoustic power output of the source, in watts?
(Note: The reference intensity I0 is 1.0 × 10-12 W/m2.)
The density of an average person is about
1) 480 kg/m3 (30 lb/ft3). 2) 960 kg/m3 (60 lb/ft3). 3) 1920 kg/m3 (120 lb/ft3). 4) 2400 kg/m3 (150 lb/ft3). From this we can see that the volume of a 120-lb person is about 5) 1 ft3. 6) 2 ft3. 7) 3 ft3. 8) 4 ft3. 9) not enough information to estimate.