If car manufacturers begin using new labor-saving technology on their assembly lines, we would not expect
a. a smaller quantity of labor to be used.
b. the supply of cars to increase.
c. the firms' costs to fall.
d. individual car manufacturers to move up and to the right along their individual supply curves.
d
You might also like to view...
"Comparative advantage" is defined as a situation in which one person can produce
A) more of all goods than another person. B) more of a good than another person. C) a good for a lower dollar cost than another person. D) a good for a lower opportunity cost than another person. E) all goods for lower opportunity costs than another person.
Figure 2-1 illustrates the trade-off for a particular student between time spent studying per week and income per week from working part-time. If this student does not study at all, how much income can they earn?
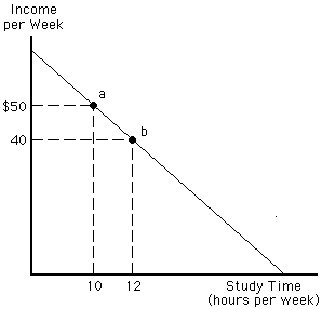
a.
$0
b.
$40
c.
$80
d.
$100
e.
$120
Giving up consumption today for consumption tomorrow accelerates economic growth by
A) having the economy produce no consumer goods.
B) increasing saving out of disposable income.
C) increasing the expected rate of inflation.
D) rapid expansion of the money supply.
Suppose that a firm maximizes its profits by producing a quantity of 20 units. The market price is $5. The firm's variable costs are $70 and its fixed costs are $40. What should the firm do in the short run? In the long run?
What will be an ideal response?