Find the general solution of the differential equation. Use C, C1, C2, . . . to denote arbitrary constants. If used, do not simplify hyperbolic functions.p'(x) = 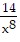 - 6 + 12x5
- 6 + 12x5
A. p = - 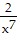 - 6x + 2x6 + C
- 6x + 2x6 + C
B. p = - 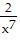 - 6x - 2x6 + C
- 6x - 2x6 + C
C. p =  - 6 + 2x6 + C
- 6 + 2x6 + C
D. p = - 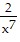 + 6x - 2x6 + C
+ 6x - 2x6 + C
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Use the given information to write an equation. Let x represent the number described in the exercise. Then solve the equation and find the number.seven more than a number is equal to twelve.
A. x = 12 + 7, x = 19 B. x + 7 = 12, x = 5 C. 7 - x = 12, x = -5 D. 7 + x = 12, x = -5
Divide the first polynomial by the second and state the quotient and the remainder.2x5 - x4 + 3x2 - x + 5, x - 1
A. Quotient: 2x4 + x3 + x2 + 4x + 3; remainder: 8 B. Quotient: 2x4 - 3x3 - x; remainder: 6 C. Quotient: 2x4 + x3 - x2 + 2x + 1; remainder: 6 D. Quotient: 2x4 + x3 + 4x2 + 3x; remainder: 8
Simplify the expression.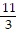 ?
? 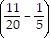
A. 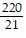
B. 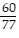
C. 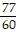
D. 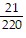
For the polynomial, list each real zero and its multiplicity. Determine whether the graph crosses or touches the x-axis at each x -intercept.f(x) = 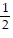 x2(x2 - 3)
x2(x2 - 3)
A. 0, multiplicity 2, touches x-axis;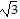 , multiplicity 1, crosses x-axis;
, multiplicity 1, crosses x-axis;
-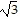 , multiplicity 1, crosses x-axis
, multiplicity 1, crosses x-axis
B. 0, multiplicity 2, touches x-axis
C. 0, multiplicity 2, crosses x-axis;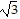 , multiplicity 1, touches x-axis;
, multiplicity 1, touches x-axis;
-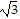 , multiplicity 1, touches x-axis
, multiplicity 1, touches x-axis
D. 0, multiplicity 2, crosses x-axis