Briefly explain the difference between price effect and output effect, and discuss how they are related to the marginal revenue and demand curves for a monopolist.
What will be an ideal response?
To sell more output, the monopolist must accept a lower price on all units sold—the price effect; the monopolist receives additional revenue from the new unit sold—the output effect, but less revenue on all the units it was previously selling. Thus, the marginal revenue curve for the monopolist always lies below the demand curve.
You might also like to view...
The economy pictured in the figure below has a(n) ________ gap with a short-run equilibrium combination of inflation and output indicated by point ________. 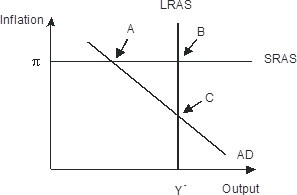
A. recessionary; B B. recessionary; C C. recessionary; A D. expansionary; A
According to Keynesians, an increase in the money supply will have its greatest impact on GDP when the aggregate demand curve intersects:
a. the vertical portion of the aggregate supply curve. b. the upward sloping portion of the aggregate supply curve. c. the horizontal portion of the aggregate supply curve. d. either the upward sloping or the vertical portions of the aggregate supply curve. e. either the horizontal or vertical portions of the aggregate supply curve.
The marginal fixed cost of a firm:
a. is a positive constant irrespective of output level. b. declines as output is increased because a fixed numerator is divided by an ever-growing denominator. c. generally increases as output is increased. d. is equal to average variable cost and average total cost at their minimum points. e. is always equal to zero and is therefore ignored by economists.
The idea that it takes 80 percent of your time to clean up the last 5 percent of your house illustrates that
A) the marginal cost of cleaning up slopes downward. B) the marginal cost of cleaning up slopes upward. C) the marginal benefit of cleaning up is constant. D) the marginal benefit of cleaning up slopes upward.