Discuss the role of claudins in the structure and functions of tight junctions. Propose what might change for a tight junction in which charged amino acids in the claudin large extracellular loop are mutated to nonpolar amino acids
What will be an ideal response?
Answer: Claudin extracellular loop domains form homophilic interactions that are a barrier to paracellular transport through intercellular spaces between epithelial cells. Charged amino acids in the claudin large extracellular loop form ion-selective pores that allow the passage of specific ions through the barrier. Mutation of the charged amino acids to nonpolar ones would create a more hydrophobic region that could block ion transport but allow passage of nonpolar substances that fail to pass through wild-type claudins. This would change the barrier function of the tissue and could affect the health of the organism. Recessive mutations in one type of claudin result in an inherited disorder characterized by severe Mg2+ and Ca2+ imbalance.
You might also like to view...
Given this information from one element in the periodic table of elements, the number of neutrons and protons is
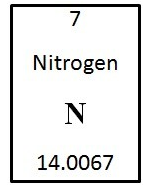
A. 7, which is also the atomic mass.
B. unable to be determined with the information provided.
C. 14, which is also the atomic mass.
D. 14, which is also the atomic number.
E. 7, which is also the atomic number.
The chloroplasts of modern plants are thought to have been derived according to which sequence?
A) cyanobacteria ? green algae ? green plants B) cyanobacteria ? green algae ? fungi ? green plants C) red algae ? brown algae ? green algae ? green plants D) red algae ? cyanobacteria ? green plants E) cyanobacteria ? red algae ? green algae ? green plants
Which phylum has members that exhibit radial symmetry, with their body parts arranged regularly around a central axis?
a. Porifera b. Cnidaria c. Chordata d. Platyhelminthes
An example of an important biological molecule that may contain the -NH2 group is:
A) a glucose molecule. B) steroids. C) a triglyceride. D) an enzyme. E) a starch.