Describe the formative characteristics of advection fogs, valley fog, evaporation fog, and radiation fog along with their usual locations
What will be an ideal response?
Fog is a cloud layer on the ground with visibility restricted to less than 1 km (3,300 ft). Radiation fog results when radiative cooling of the surface chills the air directly above the surface to the dew-point temperature. Advection fog occurs when air in one place migrates to another place where the conditions are right for saturation. For instance, when warm, moist air moves over a cooler ocean current. Valley fog is a type of advection fog, which results from cooler, denser air settling in low-lying areas. Similarly, upslope fog forms as moist air is lifted due to topography and, as a result, adiabatically cools. Evaporation fog forms when cold air lies over a warm water body and water molecules evaporate from the water surface into the cold, overlying air.
You might also like to view...
On each figure use a blue pencil to draw in streams, using arrows to show the direction of stream flow. Note that there is a main stream in the valley and there are at least two tributary streams or creeks. How do the contour lines indicate the direction of flow?
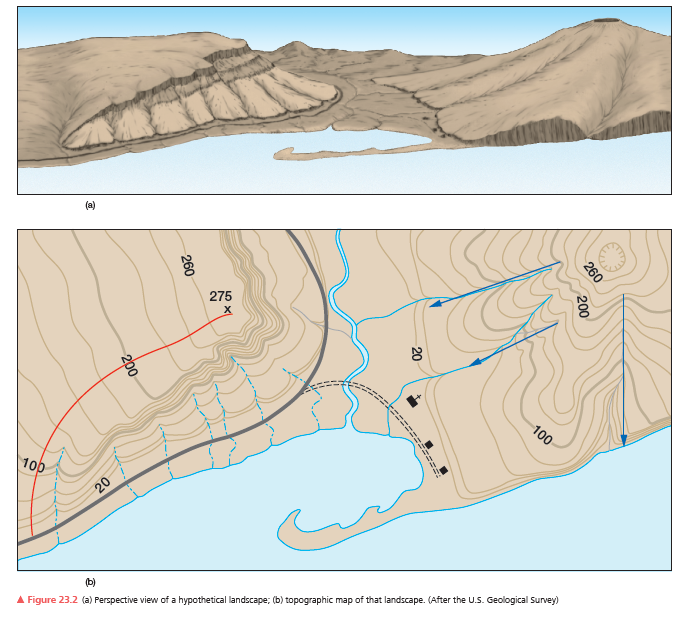
What will be an ideal response?
Which soil horizon contains humus?
a. A b. B c. C d. D e. O
If the temperature at the surface of Earth (at sea level) is 40°C, what is the temperature at 2000 m if the normal lapse rate is 6.4°C/1000 m?
A) 33.6°C B) 46.4°C C) 60°C D) 52.8°C E) 27.2°C
Species introduced to areas they are not native to can cause environmental damage by outcompeting the local fauna or flora. These are generally referred to as ________
A) Invasive species B) Aggressive groups C) Encroaching guests D) Intrusive families