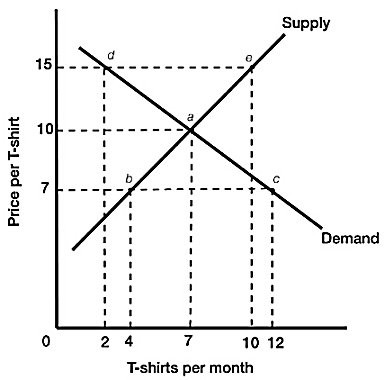
 Figure 3.3 illustrates the supply and demand for t-shirts. If the actual price of t-shirts is $15, we would expect that:
Figure 3.3 illustrates the supply and demand for t-shirts. If the actual price of t-shirts is $15, we would expect that:
A. demand will decrease until quantity demanded equals quantity supplied.
B. supply will increase until quantity demanded equals quantity supplied.
C. price will decrease until quantity demanded equals quantity supplied.
D. there will be no change in the price since the market is in equilibrium.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Which of the following would cause an increase in the equilibrium price and an increase in the equilibrium quantity of watermelons?
A) an increase in supply and an increase in demand greater than the increase in supply B) an increase in demand and an increase in supply C) a decrease in demand and an increase in supply D) an increase in supply
During hyperinflation, exploding inflation causes real money demand to
A) fall over time, and this additional monetary change makes money prices rise even more quickly than the money supply itself rises. B) increase over time, and this additional monetary change makes money prices rise even more quickly than the money supply itself rises. C) fall over time, and this additional monetary change makes money prices decrease even more quickly than the money supply itself rises. D) increase over time, and this additional monetary change makes money prices decrease even more quickly than the money supply itself rises. E) fall over time, and this additional monetary change makes money prices decrease even less quickly than the money supply itself rises.
The derived demand curve for a good component will be more inelastic
A) the larger is the fraction of total cost going to this component. B) the more inelastic is the demand curve for the final good. C) the more elastic are the supply curves of cooperating factors. D) the less essential is the component in question.
When people like yourself hold money in the event that a good opportunity may arise, such as the opportunity to purchase high interest-bearing assets, economists classify this money as satisfying your
a. precautionary motive b. transactions motive c. speculative motive d. liquidity motive e. investment motive